Let’s say your company is about to launch new products across different countries simultaneously. A PEST analysis reveals upcoming regulatory changes in one region and a rising competitor trend in another. Thanks to this early insight, your team adapts the strategy to secure faster approvals and refine your product to stand out.
That’s the power of PEST analysis.
It is a powerful guide for organizations to understand external factors influencing their business environment. The analysis framework considers four major external factors; political, economic, social and technological influences. When you acknowledge the influence of these external factors beforehand, you make informed decisions, set priorities and plan for future growth with confidence.
What is PEST analysis?
PEST evaluation breaks down external factors affecting a business into four categories:
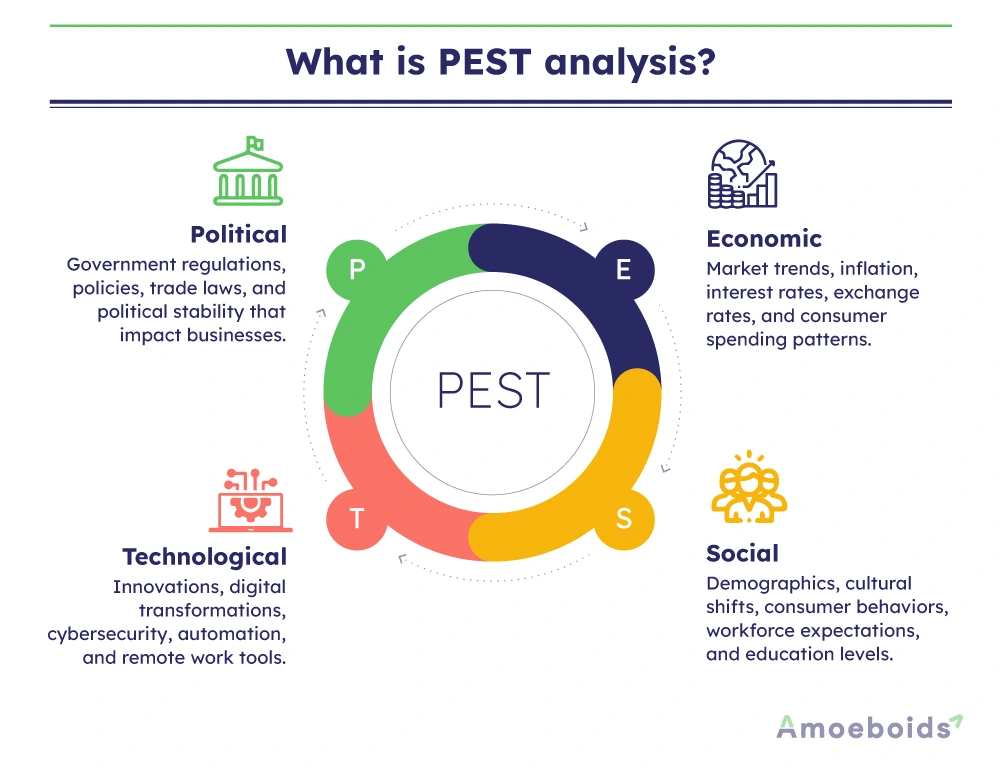
- Political: Government regulations, policies and stability
- Economic: Market trends, inflation, interest rates
- Social: Demographics, consumer behavior, cultural shifts
- Technological: Innovations, digital transformation, industry advancements
Some businesses expand this framework to include legal and environmental factors, calling it PESTLE analysis. We will define and look at PESTLE analysis examples later in this article.
Now, let’s break down the four key components of business PEST analysis with examples.
Political factors (P)
Political factors, even minor policy changes, can significantly disrupt business operations. Some instances include:
- Employment regulations: labor laws, such as minimum wages and workplace safety rules that can increase hiring costs
- Environmental policies: Are strict sustainability regulations on the horizon? If yes, analyze how they will affect production costs.
- Government policies: Check the history of the local government’s business-friendly environment. Are there restrictive laws that could slow growth?
- Taxation: Are new tax policies or higher corporate taxes likely to affect profitability?
- Trade restrictions and tariffs: Will import/export duties impact your supply chain or pricing strategy?
Economic factors (E)
A strong economy means more spending. But what if it is slowing down? It might require your company to adjust pricing, marketing or investment strategies. When analyzing economic factors, consider:
- Market growth: Expanding or slowing down?
- Inflation and interest rates: These factors can significantly affect your costs, pricing and consumer spending
- Exchange rates: Can currency fluctuations impact your profits by impacting ongoing imports or exports?
- Consumer spending patterns: People cutting back on non-essential expenses is not good. The rise of disposable income is an ideal condition.
- Labor market conditions: Are skilled workers easy to find and retain without constantly battling through rising wage concerns?
Social factors (S)
Consider the social environment of your industry’s market. Identify preferences of your local consumers and employees that bring them to your business, which will require analyzing:
- Consumer preferences: New preferences related to your product or service (e.g., healthier food vs cheap food).
- Demographics: Is it aging, growing, or shifting towards urban living?
- Division of wealth: Is there a large wealth gap that could affect the growth in consumption rate during inflation times?
- Workforce expectations: Expectations of your employees from the job market and typical work arrangement (e.g., flexible work, better benefits, or ethical company values).
- Education and skill levels: Can you find qualified employees or do you need to invest in training?
Technological factors (T)
Technology can be an opportunity or a challenge, depending on how well you adapt your operations. Some key areas to focus on include:
- Automation and AI: What are the potential applications of new technologies and AI on your business operations to improve efficiency and cut costs?
- Cybersecurity: How will you work in line with data protection regulations and avoid potential cyber threats?
- Innovation: Can you leverage new technologies to open new markets for your business?
- Remote work and digital transformation: Are you using the right tools to take maximum advantage of your remote work setting?
Let’s see how analyzing these factors before entering a new market or introducing a new product to your existing customer base can benefit your enterprise.
Benefits of PEST analysis
Despite having a strong workforce and advanced infrastructure, failing to anticipate the impact of external forces can derail your business strategy. In this regard, PEST analysis guards you against market shifts, policy changes and economic downturns by:
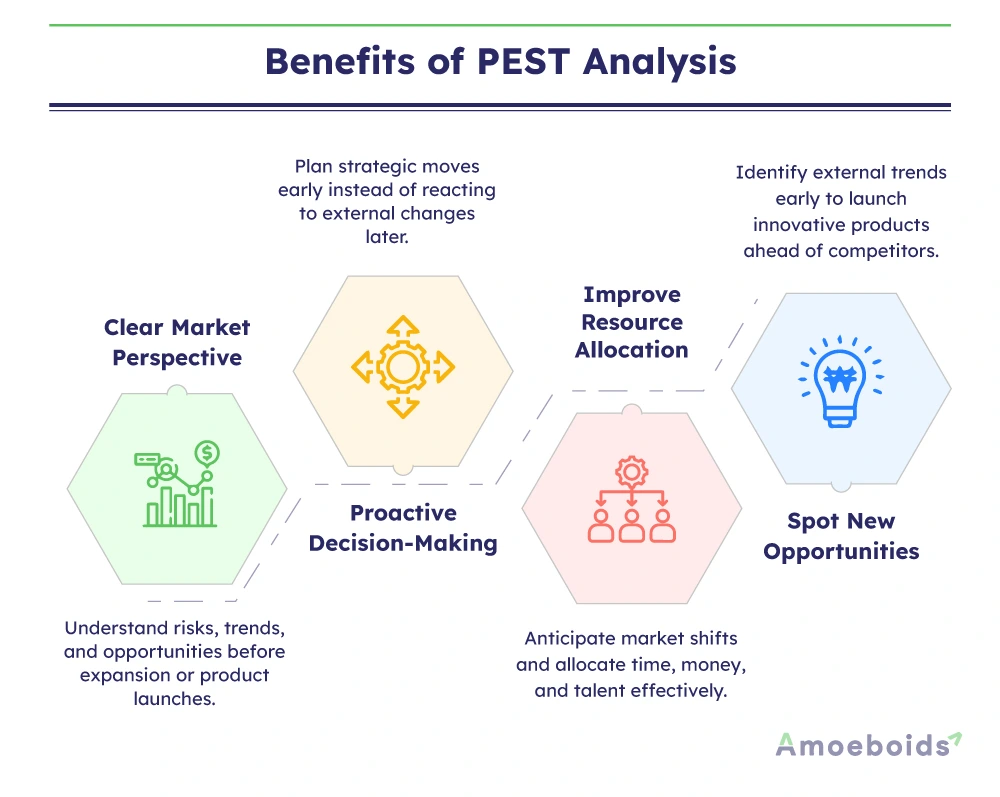
1. Providing a clear market perspective
Markets can be unpredictable for a new business. With a PEST analysis, you can understand possible risks, emerging trends and areas of opportunity before making big moves.
For example, a fintech startup planning to launch a digital wallet in an emerging economy should carry out a PEST analysis to gauge the risks of non-compliance or potential operational changes due to external factors.
2. Encouraging proactive strategic decisions
Manufacturers reacting slowly to new technological adoptions see a 17% decline in productivity compared to early adopters. PEST analysis helps you make such strategic moves in advance to gain a competitive edge. Instead of reacting to events, you take proactive actions with clarity.
Another business PEST analysis example is of a retail brand expanding internationally. A PEST analysis shows that consumer spending is dropping in some regions due to economic uncertainty. The brand will likely shift focus to budget-friendly product lines and offer economical deals tailored for the budget market.
3. Helping spot new opportunities for product development
PEST analysis helps you map external shifts, such as policy changes, tech advancements, or social trends. These insights spark product ideas for potential future demands. Your brand can launch next-gen products ahead of the curve, dominate niche markets, and hit revenue goals faster than traditional go-to-market cycles.
For instance, look at this business pest analysis example about Electric Vehicle (EV) electrical energy storage solutions. The team finally identified battery technology as the best solution using PEST analysis and analytical network process calculation tools.
4. Improving resource allocation
Many businesses struggle with allocating time, money, and talent where it matters. With a PEST analysis, you can anticipate the market in advance to adjust and manage your resources efficiently.
Let’s say a pharmaceutical company needs to plan marketing, production and distribution to launch a new drug. A PEST analysis might show that an upcoming change in healthcare policies will fast-track approvals for certain medications. The company can then shift resources to speed up regulatory approvals instead of spending excessively on market testing.
In business, external factors change whether you prepare for them or not. Next, let’s take a business PEST analysis example of one of the world’s largest beverage and snack companies. You will understand how to anticipate market shifts and make informed choices to keep your organization agile and ahead of the competition.
PEST analysis example
PepsiCo, one of the world’s largest beverage and snack companies, operates in over 150 countries, including India. Let’s do a quick PEST analysis to see what external factors constantly influence its global business expansion strategies.
Political factors
- Governments frequently revise tax policies, which impact PepsiCo’s pricing and profit margins.
- The company has to deal with strict labor laws in certain countries with a constant battle to keep operational costs under control.
- Political instability and civil unrest can disrupt PepsiCo’s supply chain and delay expansion plans. The company has to assess geopolitical risks before entering new markets.
Economic factors
- Despite a good global economy, the lingering threat of recessions varies from one country to another. This can slow consumer spending on non-essential products, including soft drinks and snacks.
- If local currencies weaken against the U.S. Dollar, PepsiCo may face higher import costs for ingredients. The brand should always be ready for a reevaluation of its sourcing and pricing strategies.
Social factors
- Consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the health risks associated with sugary beverages. This shift in preference may reduce the demand for carbonated drinks and push PepsiCo to focus more on healthier alternatives like bottled water and fruit juices.
- The rise in health-conscious lifestyles has led to a growing demand for plant-based and functional beverages. PepsiCo must invest in product diversification to cater to evolving consumer preferences.
- Cultural differences across regions influence marketing campaigns. PepsiCo must adapt its branding and advertising strategies to resonate with local consumers.
Technological factors
- There should be constant innovation in beverage manufacturing with automation and AI-driven quality control to maintain high production efficiency.
- Further advanced use of IoT and data analytics in manufacturing and distribution helps optimize supply chain management, ensuring timely delivery and inventory tracking.
- E-commerce and direct-to-consumer sales channels have reshaped how PepsiCo reaches its customers. The company must continue investing in digital marketing and online sales platforms to stay competitive.
PepsiCo’s approach shows how businesses can use PEST evaluation to stay ahead of market changes and drive growth. However, PEST analysis has its limitations. Before we look at them in the FAQs, let us understand the difference between PEST & PESTLE.
What is the difference between PEST and PESTLE analysis?
PESTLE is a term that closely resembles PEST evaluation; however, there are a few crucial differences between them. Defining PESTLE involves two additional factors, legal and environmental. Let’s understand PESTLE analysis with examples to see how it differs from PEST evaluation.
Here’s a clear comparison between the two with supporting examples:
| Aspect | PEST Analysis | PESTLE Analysis |
| Definition | Focuses on four key external factors: Political, economic, social and technological | Expands on PEST by adding Legal and Environmental factors for a broader perspective |
| Scope | Provides a basic macro-environmental analysis useful for most businesses | Offers a detailed macro-environmental analysis, ideal for industries affected by regulations or environmental concerns |
| Legal factors | Not included in the analysis | Examines laws, regulations and legal policies affecting business operations |
| Environmental factors | Not considered | Evaluates climate change, sustainability laws and environmental regulations that impact industries like energy, manufacturing and retail |
| When to use? | Best for general market analysis or businesses that are not heavily regulated | Ideal for industries like healthcare, finance, real estate, or manufacturing, where laws and environmental policies play a crucial role |
| Example | A tech startup launching a new app might use PEST to assess market conditions | An automobile company expanding into electric vehicles might use PESTLE to evaluate government EV policies and environmental regulations |
Conclusion
PEST analysis is a powerful way to understand how political, economic, social, and technological factors can influence your business strategies to achieve stable growth over the years. There can be new policies, economic shifts, changing consumer trends, or emerging technologies. By utilizing PEST evaluation methods, you can spot opportunities, manage risks and plan ahead with confidence. If you want to include legal and environmental factors too, consider PESTLE analysis.
Though these analysis concepts are straightforward, applying them for evaluation can be tricky. Take any PEST analysis example for a small business, learn its applications, and use it for your business to make informed decisions and stay ahead of the curve.
FAQs
1. What are the limitations of PEST analysis?
PEST analysis focuses only on external factors, ignoring internal business operations. It can be time-consuming and predictions may become outdated quickly. Additionally, interpreting data subjectively can lead to biased decisions, making it crucial to pair PEST analysis with other strategic tools.
2. How does PEST analysis affect business?
PEST analysis helps businesses understand market conditions, anticipate risks and identify growth opportunities. It influences decision-making, resource allocation and long-term planning, ensuring companies stay adaptable to external changes like economic trends, policy shifts and evolving consumer behavior.
3. What are the problems with PEST analysis?
PEST analysis requires extensive research, and inaccurate or outdated data can lead to flawed conclusions. It also doesn’t provide direct solutions – businesses must interpret findings correctly and integrate them with other strategic frameworks for effective decision-making.
4. How can PEST analysis be applied to make decisions?
Businesses use PEST analysis to assess risks, refine strategies, and plan market entry or expansion. By evaluating political, economic, social, and technological factors, companies can make informed decisions about investments, product launches, and operational adjustments to stay competitive.