Ever wondered how software can make decisions and take actions on its own, without needing a human to click every button? That’s the magic of AI agents. From virtual assistants that schedule meetings to systems that reroute deliveries in real time, AI agents are quietly transforming how work gets done. But what exactly is an AI agent, and how is it different from regular software?
An AI agent can work as a smart assistant that knows what needs to be done and can take action without requiring constant human intervention. Though it sounds exciting, it is important to understand what an AI agent is and how it works to acknowledge its potential in expanding your business horizons.
What is an AI agent?
An AI agent is a software program that can autonomously act to complete tasks without requiring a human in the loop. AI agents utilize advanced natural language processing and machine learning techniques to process information from their environment to choose between available options. Unlike regular software that just follows simple instructions, an AI agent can adjust its actions and use gathered data to meet predetermined goals. This dynamic ability makes AI agents powerful tools for any organization that wants to work smarter. Agents in AI are predominantly used in software development, coding tools, virtual chats and online shopping platforms.
Let’s take an example of a virtual assistant. It answers customer queries and learns to solve problems based on every interaction. A logistics company can use such an AI agent to manage shipments, predict delays and automatically adjust delivery routes without manual intervention.
Are all AI agents the same? No, they come in different types, with unique capabilities depending on the complexity and type of task.
Types of agents in AI
AI agents can be categorized based on their decision-making processes, their intended purpose and how they arrive at outcomes. Types of agents in AI can range from simple rule-based systems to advanced learning systems powered by large language models (LLMs) that adapt and improve over time. Below, we will discuss five unique types of AI agents to help you determine which is the best fit for your business needs.

1. Simple reflex agents
Simple reflex agents react directly to what they sense without using memory or thinking about past experiences. They work on a simple if-then rule. If something happens, then act in a certain way. They are like thermostats that turn on the heating when the room gets too cold. As they don’t have any analytical capabilities, these agents only work well in environments where everything is fully visible and predictable.
Simple reflex AI agents examples: Vacuum cleaning robots, thermostats, automatic doors, traffic light control
2. Model-based reflex agents
Model-based reflex agents can react and also build a small memory of what’s happening around them. They use this saved memory to make better decisions when the environment changes or information is missing. They constantly update their internal model with new information to act even when they can’t see everything at once.
Model-based reflex AI agents examples: Robotics, gaming AI, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation
3. Goal-based agents
Goal-based agents react, remember and plan. These agents are driven by a goal and they think through the best actions to reach it. The structure of such agents in AI is programmed to evaluate different choices and pick the one that moves them closer to their goal. That’s why goal-based agents are much more flexible and powerful than simple reflex agents.
Goal-based AI agents examples: Roomba, Rovo agents in Atlassian Jira (a project management software), video game AI
4. Utility-based agents
Utility-based agents work based on goals but also choose the best possible way to achieve them. They measure the degree of satisfaction or utility with each possible outcome before taking action. So, they evaluate several factors like speed, cost or satisfaction.
Utility-based AI agents examples: Controlling robots in various tasks, navigation in autonomous vehicles, performance optimization in games
5. Learning agents
You must have noticed how Amazon recommends products based on your recent research. That’s where learning agents are in action. They learn from experience and get better over time without being reprogrammed. They can adjust to new situations, improve their performance and even create better strategies as they gather more data.
Learning agents usually combine elements from the other agent types but stand out because of their ability to grow and evolve based on what they learn.
Learning AI agents example: Personalized recommendations in e-commerce sites and streaming platforms, forecasting in financial trading, patient health data monitoring
Next, let’s look at some real-world examples to help you see how AI agents are already being used today.
AI agents examples
AI agents can encompass a wide range of functions beyond NLP. Different types of AI agents are being utilized in a variety of industries and roles. Let’s look at some real-life AI agent examples to understand how they quietly make things faster, easier and smarter.
1. Chatbots and virtual assistants
Any support bot or chatbot you see on a website is a simple or model-based agent. They answer your questions based on set rules or memory. More advanced assistants like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant are also AI agents in action.
2. Recommendation systems
When Netflix suggests a new show or Amazon recommends a product, you are being served by a learning agent. They track your behavior to improve their predictive power to impress you better next time.
3. Self-driving cars
Autonomous vehicles like Tesla’s self-driving system use a mix of model-based, goal-based and learning agents. They sense the environment, make quick decisions and adjust routes for safe travels. Such agents constantly learn from every drive to improve future performance.
4. Smart home devices
Smart thermostats like Nest don’t just turn the heat on and off. They learn your habits over time when you come home, when you sleep and adjust the temperature automatically to maximize comfort and save energy. This is another great example of a learning agent at work.
5. Fraud detection systems
Banks and financial companies use AI agents to detect suspicious transactions. These agents learn the normal spending patterns of customers and raise an alert when something unusual happens, like a sudden expensive purchase in a different country.
6. Robotics in warehouses
In big warehouses like the ones owned by Amazon, robots act as goal-based agents. They move around, pick up packages and transport them efficiently based on real-time goals like order priority and optimal routes.
Now that you’ve seen where AI agents are already making a difference, let’s go deeper into how they are structured and built to do these amazing things.
Structure of agents in AI
There are different types of agents in AI, but all have been built around a basic structure to mimic human consciousness. Let’s break it down to see how it all fits together.
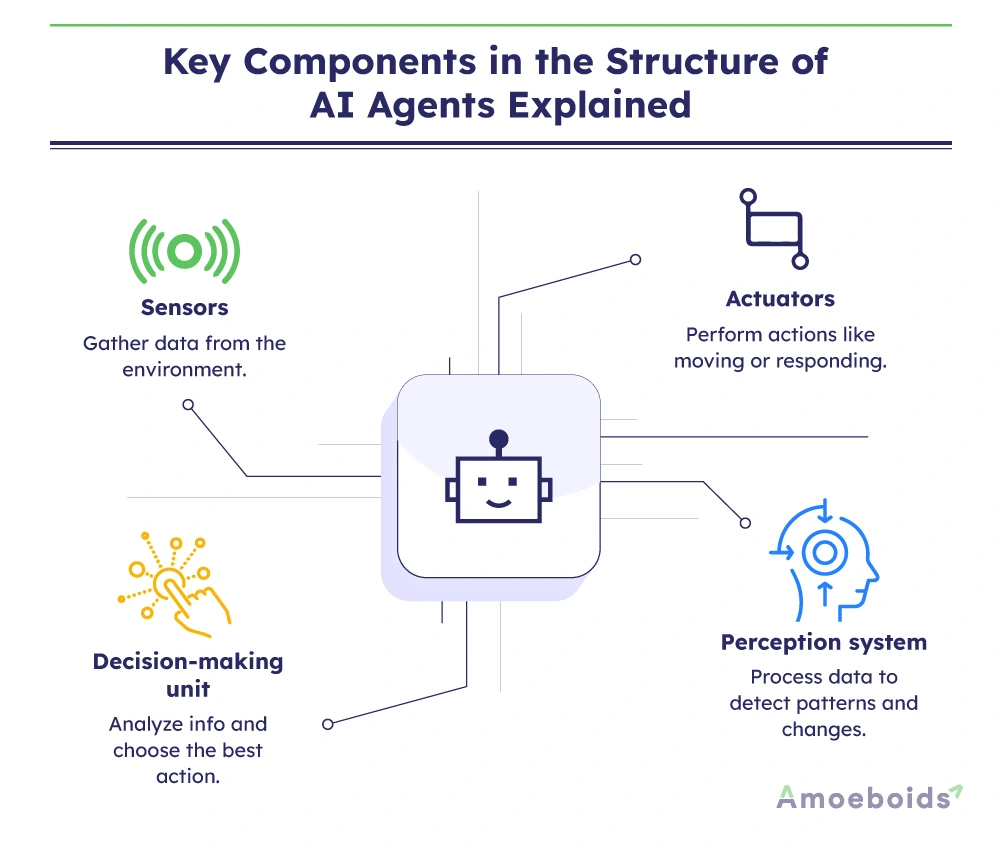
The structure of agents in AI can be divided into four key components:
1. Sensors
Think of sensors as the agent’s eyes and ears. Sensors collect information from the environment. For example, a robot vacuum uses cameras and proximity sensors to “see” furniture and walls. Similarly, a chatbot uses your typed questions as input data.
2. Perception system
Once the sensors collect information, the agent needs to make sense of it. This is where the perception system comes in. It processes the raw data and identifies patterns, changes or important elements. Without perception, the agent would have no understanding of what’s happening around it.
3. Decision-making (reasoning) unit
This is the brain of the agent. After understanding the situation, the agent must decide what to do next. It might follow simple rules (“If obstacle, turn left”) or complex logic (like evaluating multiple possible actions to choose the best one). Some advanced agents even predict what might happen next before acting.
4. Actuators (action mechanism)
After deciding what to do, the agent needs to act. Actuators are what make something happen. For a robot, actuators could be motors that move its wheels. For a software agent like a recommendation engine, the “action” could be displaying a product you might like.
Conclusion
Agents in AI are changing the way businesses work. These agents are aiding organizations in making quicker decisions, offering better services and running operations more smoothly without constant human supervision.
Understanding the structure of agents in AI and the different types available gives you a huge advantage. This clarity will help you choose the right AI agent for smarter customer service, faster logistics and more personal experiences for your users than before. Try to learn more about them to stay one step ahead of your competitors and build a wholesome product strategy for your business.
FAQs
How are AI agents used in customer service?
AI agents in customer service help you handle customer queries faster and more accurately. They can chat with customers, solve problems, offer solutions and even guide them through processes, all without needing a human every time.
What industries benefit from AI agents?
Almost every industry can benefit from AI agents. Whether you’re in retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing or logistics, AI agents help you speed up operations, offer better services and make smarter business decisions based on real-time data.
What is the difference between an AI agent and a human agent?
An AI agent works automatically based on the information it receives, while a human agent relies on experience, emotions and judgment. AI agents are faster, available 24/7 and great at handling repeat tasks without getting tired.
What are the advantages of using AI agents in business?
AI agents can boost your efficiency, save time, lower costs and improve customer experiences. They help you make better decisions, automate boring tasks and focus more on the parts of your business that really need a human touch.