You’ve got 20 tasks to tackle this week. Six need input from the analytics team, eight you can handle solo, and six require cross-functional collaboration.
Things quickly become confusing without work management tools to streamline workflows and track progress.
Work management tools are software platforms designed to simplify collaboration, organize tasks, and track progress. They replace chaos with clarity, ensuring teams stay aligned and productive. For instance, a recent report shows companies using these tools achieve 30% higher task completion rates and a 40% leap in collaboration effectiveness.
In this blog, we’ll explore the journey of work management tools from humble beginnings to modern powerhouses—and glimpse into their exciting future.
Early limitations of work management tools
The roots of work (or project) management tools trace back to the 1800s when workers used charts and diagrams to visualize work plans. These rudimentary methods laid the groundwork for structured task management but were far from efficient. Let’s explore the key limitations of early work management methods.
The manual mayhem
Before the digital age, managing work revolved around physical tools—pens, paper, and communal whiteboards. By the mid-1900s, whiteboards acted as team hubs: tasks were scribbled for all to see, much like an analog version of today’s shared task platforms. Planners, notepads, and filing cabinets became essential fixtures in workplaces.
But this era came with significant drawbacks:
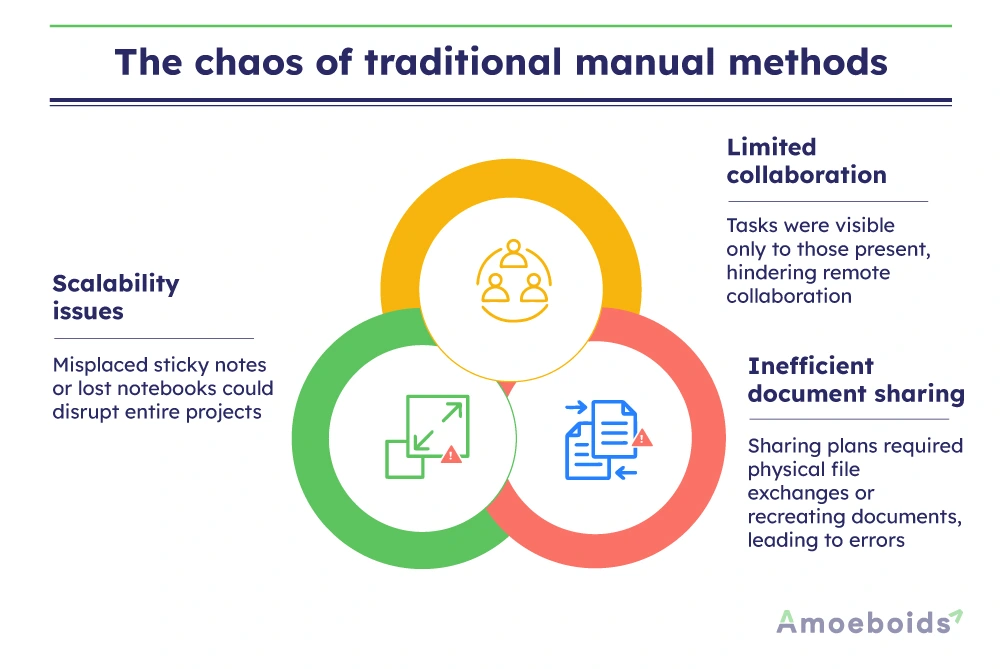
Scalability issues:
A misplaced sticky note or a lost notebook could derail entire projects.
Limited collaboration:
Tasks were only visible to those physically present, leaving remote team collaboration almost impossible.
Inefficient document sharing:
Sharing a plan meant physically handing over a file or re-creating it for others—a tedious and error-prone process.
While these methods helped teams organize tasks somewhat, they couldn’t keep pace with growing workplace complexities.
The email revolution
In 1965, email was first developed at MIT as a way for users to share information on the same computer. By 1971, Ray Tomlinson revolutionized email into a tool for sending messages across networks. Over time, email became indispensable for both personal and professional communication.
For work management, email allowed teams to share plans, discuss tasks, and collaborate remotely. Imagine tracking a project via email: the project lead sends a list of tasks to the team, stakeholders add comments, and everyone replies with updates.
However, emails introduced their own set of challenges:
Overwhelming threads:
Important deadlines and updates often got buried in never-ending chains of replies.
Attachment chaos:
Files were frequently misplaced, or version control became an issue.
Disjointed communication:
Teams struggled to maintain a cohesive view of project progress without clear organization.
While email was a game-changer, it couldn’t handle modern project tracking demands.
Recognizing the inefficiencies of manual methods and email, organizations began developing digital solutions to manage workflows, collaboration, and task tracking more effectively. These tools streamlined project tracking provided real-time updates, and eliminated the chaos of scattered communication.
The introduction of digital work management tools
The rise of digital work management tools marked a significant turning point in how teams managed tasks and projects. These tools moved beyond manual methods and email constraints, offering more structured ways to plan, track, and collaborate. Let’s explore their evolution from the 1990s to the early 2000s.
The 1990s: The first generation of digital tools
The 1990s introduced the first generation of work management tools, including Microsoft Project and Lotus Notes. These platforms were pioneers in project management, providing digital options for scheduling, managing, and monitoring tasks. For the first time, teams could organize workflows without relying on physical charts or endless email threads.
However, these tools were limited in scope:
Basic functionality:
Their primary focus was project planning and communication rather than collaboration or integration.
User experience challenges:
Interfaces were clunky and difficult to navigate, requiring extensive training to use effectively.
Lack of flexibility:
These platforms operated in isolation, making integrating them into broader workflows or adapting to unique team needs difficult.
Despite these limitations, these tools laid the groundwork for more intuitive and collaborative solutions in the future.
The early 2000s: Collaboration enters the picture
The early 2000s saw a shift with tools like Basecamp and Trello, which prioritized collaboration and accessibility. These platforms transformed how teams worked together by bringing task management to the cloud. Trello’s card-based interface, for example, became a symbol of simplicity, enabling users to organize tasks visually as if sorting through a digital deck of cards.
According to a 2021 Gartner study, over 80% of workers used cloud-based work management tools to streamline their workflows. This era marked a significant step forward, making task delegation and real-time collaboration seamless.
However, challenges persisted:
Limited integrations:
Early cloud tools often functioned as standalone platforms, creating silos rather than a connected work ecosystem.
Scaling issues:
While effective for smaller teams, these tools struggled to accommodate the needs of larger organizations or more complex projects.
By the mid-2000s, it became clear that the future of work management lay in tools that could combine robust task management with agile, flexible workflows. The rise of agile methodologies and the demand for deeper collaboration drove the next wave of innovation.
The rise of agile and collaboration-focused tools
The limitations of early work management tools—lack of integration, scalability issues, and inefficient collaboration—highlighted the need for more dynamic solutions. Agile principles addressed these challenges with flexibility, iterative progress, and teamwork, transforming workflows and boosting efficiency.
Impact of agile methodologies
Agile approaches like Scrum and Kanban reshaped tools and team processes by:
Tracking progress:
Burndown charts visualized work remaining, helping teams stay on schedule.
Streamlining planning:
Sprint planning enabled manageable, short-term project goals.
Organizing workflows:
Storyboards made workflows transparent and prioritized collaboration.
Team-centric tools
Tools like Jira, Asana and monday.com took collaboration to the next level by enabling:
Real-time task updates:
Keeping teams informed and reducing miscommunication.
Workflow automation:
Simplifying repetitive processes to save time.
Seamless integrations:
Connecting with tools like Slack and Google Drive for unified operations.
By embedding agile principles, these platforms redefined collaboration, ensuring teams worked efficiently and cohesively.
The role of AI and automation in modern work management
Imagine having a work assistant who tracks your tasks, predicts potential roadblocks, and suggests solutions before you even notice them. That’s the power of AI and automation in today’s work management tools, making your workflow smarter and more efficient.
AI-powered features
Modern tools like Notion and ClickUp are equipped with AI to:
Predict project timelines:
AI analyzes data to forecast delays, helping you adjust plans proactively.
Prioritize tasks intelligently:
AI recognizes urgent tasks, helping you focus on what’s most important.
Optimize resource allocation:
AI detects when resources are lacking and adjusts project timelines or reallocates assets.
Generative AI also saves time by summarizing past project updates, so you no longer have to dig through old files to find what’s important.
Automation tools
Platforms like Zapier and Automate.io make integration seamless by automating tasks across platforms. For example, when a task is added in Trello, it can automatically update your Slack, log hours in your timesheet, and send reminders.
AI and automation reduce manual effort, boost efficiency, and improve task management accuracy. Streamlining processes helps teams stay aligned, focus on strategic work, and eliminate time-consuming, repetitive tasks.
Current trends in work management tools
Work management tools have evolved to meet the demands of modern teams, focusing on streamlined collaboration, seamless integration, and data-driven decision-making. These trends reshape how teams manage tasks, track progress, and stay connected.

Hybrid and remote work enablement
Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom bridge the gap for hybrid teams, ensuring smooth communication and task tracking regardless of team members’ locations.
Focus on user experience (UX)
Mobile-first, intuitive designs make tools like Jira, Asana accessible for all users, from tech-savvy professionals to beginners, ensuring ease of use across devices.
Integration and ecosystems
With 87% of businesses prioritizing integration, tools seamlessly connecting with CRMs, ERPs, and other platforms help create a unified workspace and streamline workflows.
Data-driven insights
Real-time dashboards in tools provide actionable insights that guide faster, smarter decision-making, helping teams stay on track and optimize performance.
These trends ensure that work management tools now offer more than just task tracking—they provide seamless collaboration, real-time insights, and efficient workflows that empower teams to work smarter, not harder.
Future trends for work management tools
The future of work management tools is powered by advancements in AI, machine learning, and immersive technologies, all aimed at enhancing efficiency, collaboration, and sustainability.
AI and machine learning advancements
AI is set to revolutionize task allocation and resource management. Tools like Jira, Automated release notes & reports leverage AI to summarise information, produce automated reports, while Wrike uses machine learning to prioritize tasks based on urgency and impact. Predictive analytics will continue to evolve, helping teams stay ahead of potential delays and bottlenecks.
Metaverse and virtual collaboration spaces
As remote work becomes more permanent, we expect more tools to create immersive virtual environments. These spaces will enable teams to collaborate as if they were in the same room, with tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams likely leading the way.
Sustainability and ethical technology
The focus on eco-friendly practices is gaining traction. Future work management tools will prioritize sustainability, reduce digital waste and ensure greener operations.
With AI, immersive environments, and ethical practices on the horizon, the future of work management tools will make work smarter, more connected, and increasingly sustainable.
From chaos to control
From pen-and-paper beginnings to AI-powered marvels, the evolution of work management tools is a testament to the shift from chaos to more control of the work environment.
Today, these tools go beyond just organizing tasks; they streamline collaboration, automate workflows, and provide real-time insights. Whether managing a small team or a large enterprise, the right tools can transform how you work, making productivity seamless and teamwork effortless.
As AI and automation continue to shape the future, work management tools are set to become even smarter and more intuitive, empowering teams to focus less on managing tasks and more on achieving goals.