Let us consider the case of a team that needs to launch a new marketing campaign. One marketing representative suggests a wide range of creative ideas, from influencer collaboration to guerrilla marketing. The other employee analyzes past campaigns instead and narrows down the selection to the most viable and cost-effective marketing campaign. The two different approaches highlight the prime difference between convergent thinking and divergent thinking.
Divergent thinking is about generating as many ideas as possible to encourage creativity, while convergent thinking sifts through all possibilities before deciding on one practical approach. While these approaches vary, they are equally important for decision-making.
In this article, we will look at convergent vs. divergent thinking and how and when to apply both methods to ensure success. But first, let’s start with the basics of understanding what convergent and divergent thinking even mean.
What is Divergent and Convergent Thinking?
In psychology, divergent thinking refers to the ability to explore many possible solutions and generate creative ideas. The definition of divergent thinking in psychology emphasizes imagination, flexibility, and originality—key traits in innovation and brainstorming.
In contrast, convergent thinking focuses on narrowing choices to arrive at the most effective solution. The definition of convergent thinking in psychology highlights logic, precision, and decision-making.
While they serve different purposes, both are essential in problem-solving and decision processes. Understanding how they differ—and when to use each—can help teams think more strategically and adaptively. Let’s explore the key differences between convergent and divergent thinking.
What is the difference between convergent and divergent thinking?
When we discuss convergent vs. divergent thinking, we are referring to two contrasting approaches to problem-solving and decision-making. Divergent thinking psychology involves exploring multiple possibilities, generating creative ideas, and thinking outside the box. It thrives on open-ended brainstorming and innovation.
On the other hand, convergent thinking psychology focuses on narrowing down choices and selecting the best solution based on logic. Both these styles of thinking are crucial for decision-making.
Here is a detailed table comparing the key differences between convergent vs. divergent thinking:
| Aspect | Convergent thinking | Divergent thinking |
| Definition | Narrowing down options to find the best possible solution | Generating multiple ideas and exploring various possibilities |
| Purpose | Focuses on logical reasoning, decision-making and problem-solving | Encourages creativity, innovation and brainstorming |
| Approach | Structured, analytical and linear | Open-ended, exploratory and non-linear |
| Mindset | Focused, critical and evaluative | Expansive, free-flowing and imaginative |
| Process | Filters, analyzes and selects the most viable option | Generates a wide range of solutions without immediate judgment |
| Use cases | Best suited for decision-making, strategic planning and efficiency-driven tasks | Ideal for brainstorming, product innovation and creative projects |
| Outcome | A single, optimized solution or conclusion | Multiple possibilities and creative solutions |
Teams must understand when and where to utilize these approaches to enhance their creativity and efficiency.
Convergent vs. divergent thinking: Which is best?
There is no inherently superior choice between divergent thinking and convergent thinking. Both psychologies are crucial for building a successful business. The key is to know when to use which approach.
For example, a fashion brand launching a new clothing line leverages both thinking styles at different stages. In the design phase, the team uses divergent thinking, brainstorming a wide range of styles, fabrics, and themes – from minimalist to sustainable fashion – without restrictions to foster creativity.
Once the ideas take shape, the production team shifts to convergent thinking, evaluating costs, manufacturing capabilities and market demand to refine and select the best designs for production. By integrating both approaches, the brand ensures a balance between innovation and practicality, allowing creativity to drive ideas and logic to guide execution.
Now, let’s explore specific scenarios where each approach is most effective.

Convergent thinking
- Narrowing down ideas to select the best solution: In cases when there are too many ideas, convergent thinking helps to narrow them down to the best approach.
- Making data-driven or logical decisions: Convergent intelligence analyzes facts, data and trends to make informed decisions.
- Solving problems with a clear right or wrong answer: Convergent thinking is ideal for situations that require a definitive solution with a logical approach.
- Optimizing efficiency and streamlining processes: Convergent thinking ensures that resources allocation is done effectively to minimize wastage.
- Developing action plans and implementing strategies: Once an idea is chosen, convergent thinking helps create a structured plan for execution to ensure measurable results.
Divergent thinking
- Brainstorming new ideas and solutions: Divergent thinking allows for the free flow of possibilities that makes it easy to come up with unique solutions.
- Exploring multiple possibilities without judgment: Divergent thinking encourages considering a wide range of perspectives and potential directions before deciding.
- Innovating new products, services, or strategies: Divergent thinking fuels innovation, which allows businesses to innovate new products and services.
- Encouraging creativity in marketing and design: Divergent thinking allows individuals to think outside the box, encouraging creativity for campaigns and designing.
- Tackling open-ended problems: Some challenges require thinking beyond traditional frameworks. Divergent thinking helps come up with effective solutions in these cases.
The best results often come from a combination of both thought processes. Teams can start with divergent thinking to generate ideas and then apply convergent thinking to refine and implement the best solutions. This dynamic approach ensures both innovation and practicality.
How to be a more convergent thinker?
Convergent intelligence requires precision and focus to find the best solution or the best strategy. Here are some effective ways to strengthen your convergent thinking skills:
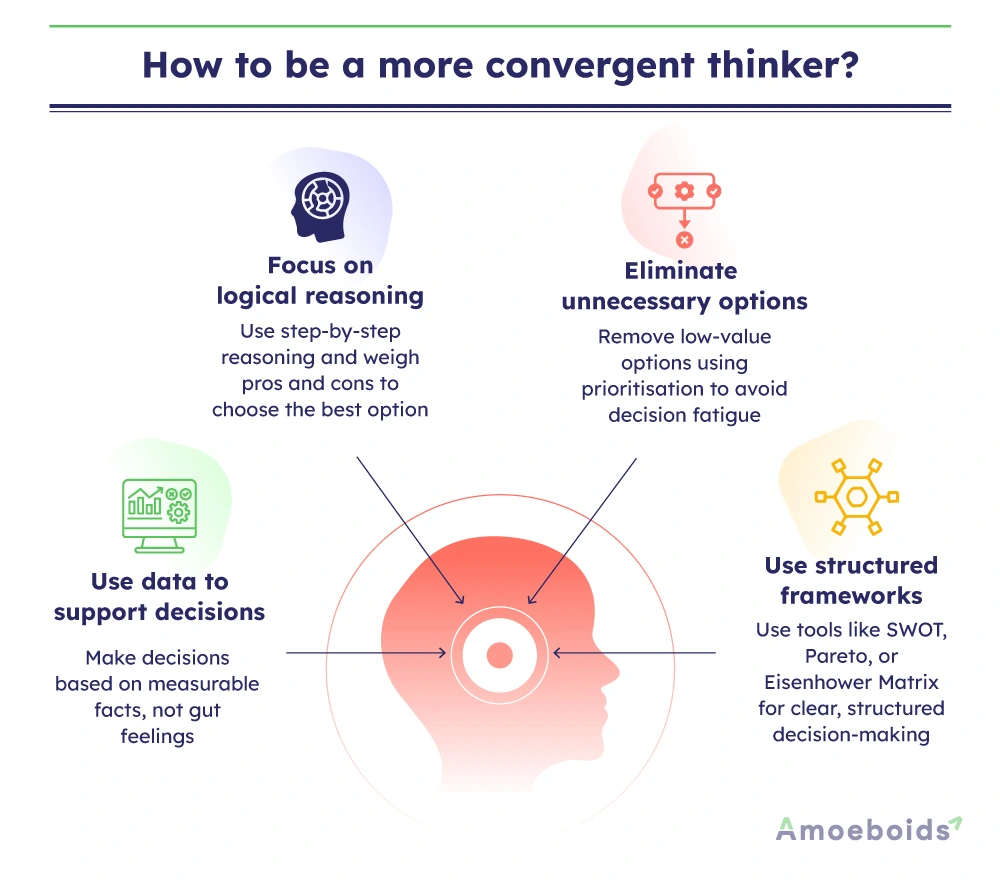
- Use data to support decisions: Convergent thinking depends on facts and data. Make decisions based on measurable data instead of using intuition or guesswork.
- Focus on logical reasoning: Train your mind to follow step-by-step reasoning rather than jumping to conclusions. Create a pros and cons list for each option to find the best solution from the potential options.
- Eliminate unnecessary options: Learn to narrow your options (using prioritization frameworks) instead of getting lost in endless options. Identify the most useful strategies and eliminate the ones that do not add value. This will take your focus where it is needed to develop the best solution.
- Use structured frameworks: Use decision-making models such as SWOT analysis, the Pareto Principle or the Eisenhower Matrix to assess problems systematically. These frameworks help assess problems objectively to come up with the best solution.
Practicing these techniques can improve your ability to think logically and solve problems efficiently.
How to be a more divergent thinker?
Being a divergent thinker, you must devise out-of-the-box solutions that can solve your problems. Here are some effective ways to strengthen your divergent thinking skills:
- Embrace curiosity and ask what-if questions: Engage with open-ended questions such as:
- What if we tried a completely different approach?
- What if we combined these two ideas?
- What would happen if there were no limitations?
This will help you come up with creative solutions and enhance creativity.
- Brainstorm without judgment: Do not self-censor your ideas while brainstorming. Instead, focus on free thinking and write down every possible idea to solve the problem. With more ideas, there is a greater chance of finding an innovative solution.
- Change your perspective: Looking at problems from different angles can lead to unique solutions. Imagine solving a challenge from different perspectives to come up with fresh insights.
- Use visual tools: Employ mind mapping tools to organize your thoughts and explore multiple angles of an idea. It will help you connect ideas and come up with valuable solutions.
By incorporating these habits into your daily routine, you can train your brain to think more creatively and explore unconventional ideas.
Conclusion
Convergent and divergent thinking both have unique uses and applications. While certain situations demand a clear course of action and require convergent intelligence, others can only be resolved by embracing the creativity and free flow of divergent thinking.
Additionally, in certain cases, combining the two is the best approach. The team can brainstorm ideas using divergent thinking and then narrow them down to the best ones with a convergent thinking approach.
However, remember that to be a convergent thinker, you must employ structured frameworks and use data to back up ideas. Similarly, to be a good divergent thinker, it is crucial to brainstorm without judgment and embrace curiosity.