In the high-tech and data-driven world, consumers trust businesses to maintain exceptional safety standards and quality assurance. A seemingly inconsequential bug or glitch in the system can have devastating consequences. One example that comes to mind is the Boeing 737 MAX’s Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS). A combination of faulty hardware and flawed MCAS software resulted in two fatal airplane crashes.
Investigations revealed that Boeing’s system tests had fallen short of accepted industry-quality standards. This scenario highlights the need for more rigorous testing methods and why businesses cannot compromise on quality assurance (QA). This is even more critical if you are launching a new app, as the last thing you want is for users to bombard you with complaints about glitches, slow loading times or broken features.
A report by Tricentis found that software failures caused an estimated $1.7 trillion in financial losses in 2017 alone. That’s how costly skipping quality assurance services can be. It can cost you lost customers, a damaged reputation and expensive reworks.
But what exactly is quality assurance, and why does it matter? In this blog, you’ll learn how QA ensures products meet high standards, its role in Agile workflows and how to integrate it effectively into your operations to prevent costly mistakes.
What is quality assurance: A comprehensive definition
Quality assurance ensures that a product or service meets predefined standards before it reaches the customer. It’s a proactive approach focused on preventing defects rather than just identifying and fixing them. In agile development, QA means maintaining consistent quality across sprints, ensuring every release is free from major flaws.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is key to shaping quality assurance practices and outlining the implementation processes. QA is often linked to the ISO 9000 standard, which many companies adopt to establish and maintain an effective quality assurance system.
For example, if QA is implemented properly in a car manufacturing plant, every vehicle undergoes rigorous checks – engine performance, safety measures and design accuracy – before it hits the showroom. Without QA, faulty brakes or engine failures could lead to safety risks. The same principle applies to software products and services.
Why is quality assurance important?
If you’ve ever asked, “What is quality assurance?” think of it as a process for maintaining standards in software development. Here are some ways it can help your business:
- Prevents costly errors – Catching issues early means less rework, saving you time, money and headaches.
- Builds customer trust – High-quality products make users stick around, boosting your brand’s reputation.
- Helps you follow regulations – Meeting industry standards and regulations helps you avoid legal trouble.
- Makes everything run smoother – Strong quality assurance services streamline workflows and cut down on delays.
The role of quality assurance in software development and product delivery
Think of quality assurance as the safety net that keeps software running smoothly. When you make it a part of every step in software development, you catch issues early instead of scrambling to fix them later. That means fewer headaches, better products and happier customers.
Key roles of quality assurance:
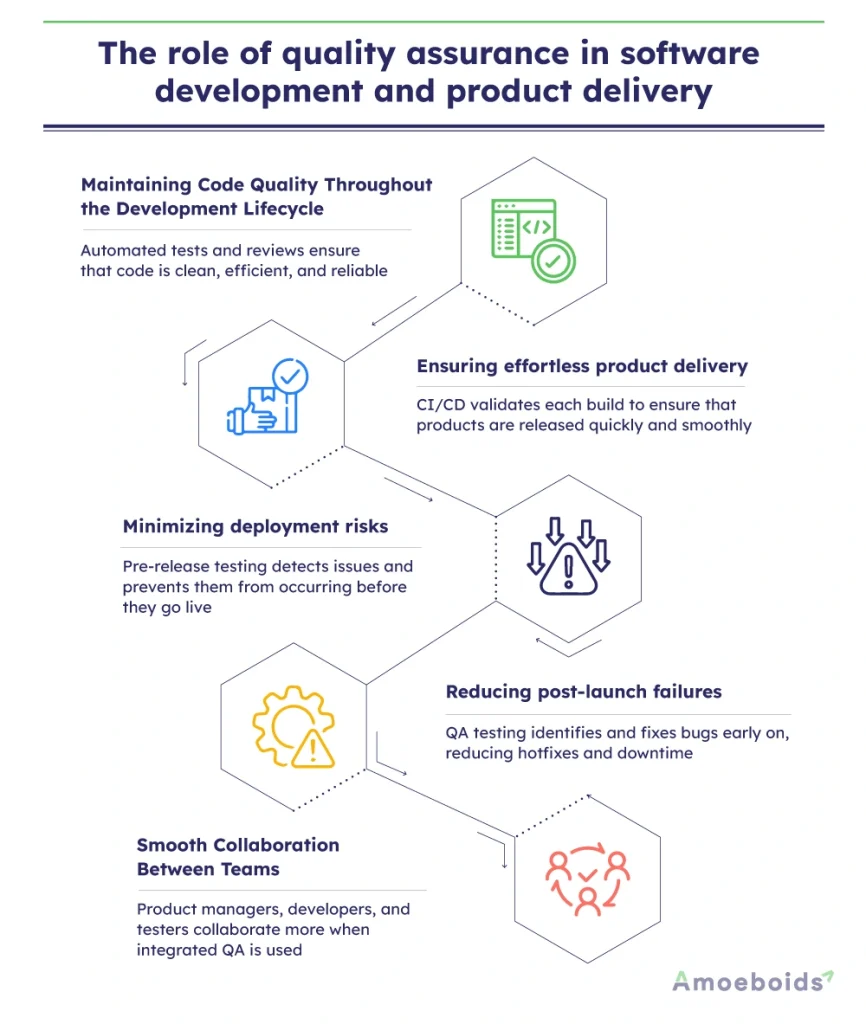
- Maintaining code quality throughout the development lifecycle: Quality assurance processes such as automated testing and code reviews ensure that software is written efficiently.
- Ensuring effortless product delivery: Through continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD) practices, quality assurance teams validate every build before release.
- Minimizing deployment risks: Before a software release, QA teams conduct release testing to verify that the update doesn’t introduce new issues.
- Reducing post-launch failures: Rigorous quality assurance testing ensures that major bugs are fixed before product delivery, reducing post-launch hotfixes, downtime and damage to customer satisfaction.
- Smooth collaboration between teams: By integrating quality assurance services into software development, developers, testers and product managers work in sync.
QA goes a long way toward delivering an excellent product or service.
Quality assurance vs. quality control
Both quality assurance and quality control (QC) ensure the reliability of software products, but they serve different purposes. The table below highlights the key differences between the two:
| Aspect | Quality Assurance | Quality Control |
| Definition | A proactive process that ensures quality by refining software development methodologies. | A reactive process that identifies and fixes defects in software products before product delivery. |
| Focus | Focuses on improving quality assurance processes to prevent errors. | Focuses on identifying and fixing issues in the final product. |
| Timing | Implemented throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC). | Conducted after the software is developed but before final product delivery. |
| Approach | Preventative. Improves quality assurance processes to avoid issues. | Corrective. Detects and resolves defects before product delivery. |
| Example | Implementing automated testing and continuous integration (CI) to enhance code quality. | Performing unit testing, functional testing and user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure the software is bug-free. |
Examples of quality assurance in real-world application
Quality assurance has become an integral part of business operations today. Examples can be found in brands across almost all sectors:
1. Agile development and continuous testing in Jira
If your team uses Jira for project management, you know how crucial it is for issue tracking and sprint planning. QA processes in Jira ensure that updates don’t break existing workflows. Through automated testing and continuous integration (CI), every new feature is checked for stability before deployment so your team doesn’t experience frustrating bugs after a product update.
2. Banking apps preventing security breaches
Security is a top priority for users of PayPal, Stripe, or mobile banking apps. Quality assurance services include penetration testing and compliance checks to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
3. Ride-sharing and food delivery apps like Uber and Zomato
Ever wondered how Uber predicts arrival times so accurately or how Zomato ensures your order updates in real time? That’s QA in action! Engineers run extensive API testing and real-world scenario testing to verify that maps, payments and order tracking work without errors.
4. Productivity tools like Trello and Asana
When managing tasks in Trello or Asana, you need a smooth drag-and-drop experience, instant updates and reliable integrations with third-party apps. Quality assurance teams continuously test these tools to make sure features like real-time sync and mobile responsiveness work as expected.
We’ve seen that QA ensures the final product meets the expectations of customers and stakeholders. It’s no surprise that it is one of the fastest-developing sectors in business management.
Predicted future trends in quality assurance: Automation, AI and beyond
As software development evolves, so does quality assurance. With the increasing demand for faster product delivery, QA is shifting towards automation, artificial intelligence (AI) and advanced analytics.
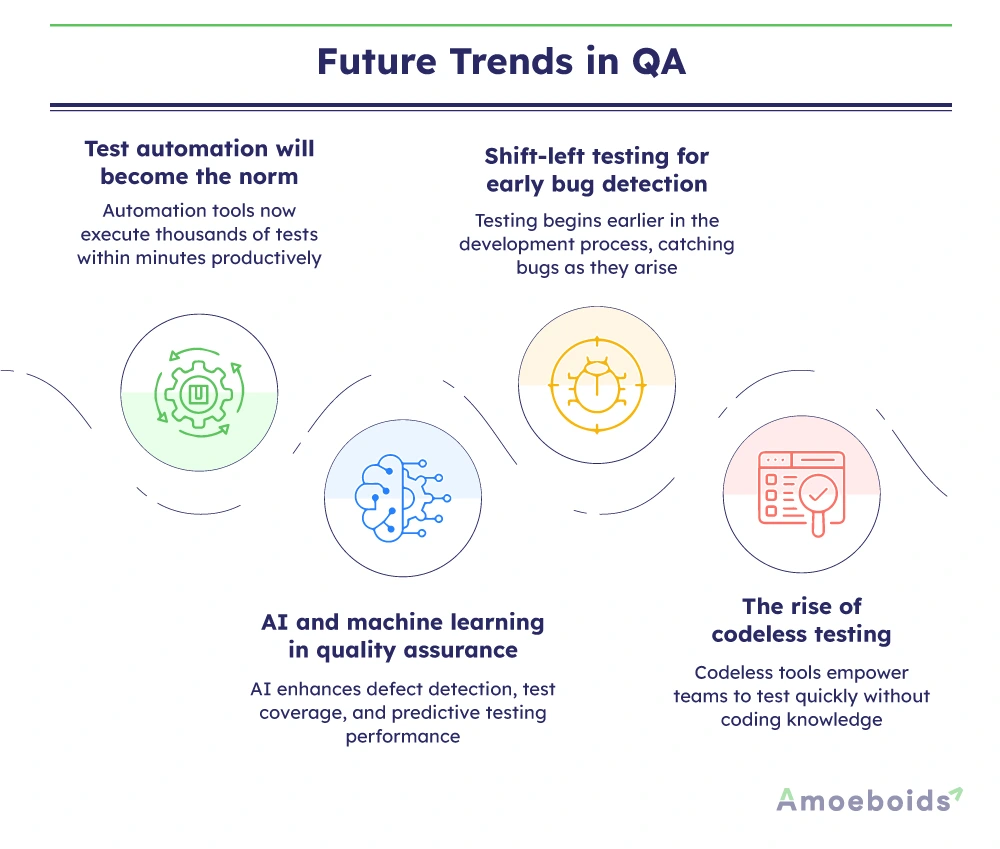
1. Test automation will become the norm
Manual testing will never disappear completely, but test automation is rapidly taking center stage. Tools like Selenium, Cypress and Playwright are helping QA teams run thousands of test cases in minutes, speeding up development cycles.
2. AI and machine learning in quality assurance
AI-powered test automation tools are improving defect detection and reducing human effort in test case generation. Predictive analytics can now identify high-risk areas in applications before testing even begins.
3. Shift-left testing for early bug detection
Quality assurance services are moving closer to the development phase with the shift-left approach. This means testing starts as soon as the code is written. Developers are increasingly using tools like SonarQube and Jest to catch issues early.
4. The rise of codeless testing
Codeless and low-code testing solutions are making QA more accessible to non-technical team members. AI creates automated tests without extensive coding knowledge, enabling faster test execution and broader team collaboration.
Conclusion: The value of investing in quality assurance for your business
QA has evolved beyond just catching bugs. It’s now about building trust, delivering a smooth user experience and making sure your software products work the way they should. If you’ve ever wondered, “What does quality assurance do?”, it’s all about spotting problems before they become expensive mistakes.
Investing in quality assurance services from the start saves you from last-minute rush, speeds up product delivery and keeps customers happy. A strong QA process means fewer security risks, better compliance with industry standards and a smoother software development lifecycle.
The future of QA means evolution. Start small, experiment with test automation and shift-left testing and refine your approach. Now you know what Quality assurance does. It’s the foundation of great software products.
FAQs
What is software quality assurance, and why is it important?
SQA makes sure your software products work the way they should. It helps keep things running smoothly, meets industry standards and gives users a hassle-free experience.
What do quality assurance engineers do?
QA engineers design and implement QA processes, conduct automated and manual testing and ensure that software products meet development lifecycle requirements before product delivery.
What does a quality assurance program include?
A QA program includes test planning, test automation, performance testing, security testing, compliance checks and defect tracking to ensure high-quality software products.
What does a quality assurance analyst do?
A QA analyst evaluates software functionality, creates test cases, executes test automation and reports defects to improve software development quality and efficiency.


