When evaluating your company’s product offerings, assessing each product’s contribution to your bottom line is important. Product portfolio management is a critical skill for ensuring that the time, budget and talent you invest in your business yield proper returns.
A Boston Consulting Group study found that excessive product complexity can increase procurement costs by 2% to 5% of goods sold (COGS). That’s a significant hit to profitability, especially when the wrong products take up valuable time, budget, and talent.
Instead of inefficiently managing too many initiatives at once, product portfolio management helps you prioritize, optimize and make strategic decisions about which products to nurture, which ones to scale and which ones to retire.
In this blog, we’ll cover:
- What is product portfolio management?
- How to build a strong product portfolio strategy?
- What are the challenges and some examples of product portfolio management?
Let’s bring some clarity and direction to your product ecosystem.
What is a product portfolio?
James Chen, a seasoned market strategist, explains:
“A product portfolio is the collection of all the products or services offered by a company, each with a different growth rate and market share.”
Product portfolios are generally classified depending on the range and nature of a brand’s products and services. A diversified portfolio comprises distinct and unrelated products and services, while a line portfolio refers to products and services that are developed to support a core or flagship product.
The classification is fluid, with some brands incorporating more than one type of strategy to develop and offer their product portfolio. Tech giant Apple manages a hybrid line-diversified portfolio to develop and sell a variety of products, all under the overarching umbrella of its proprietary code.
Let’s examine the concept of product portfolio management next.
What is product portfolio management?
Product portfolio management is a comprehensive strategy for overseeing a company’s entire product lineup. It ensures that all products align with your brand’s business goals, maximize profitability, and optimize resource allocation. A good portfolio management strategy will help your business determine which products to invest in, scale or discontinue based on metrics such as their market performance, growth potential and strategic value.
Portfolio management also involves evaluating products across different lifecycle stages:
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
It also considers factors like customer demand, competition and internal capabilities.
Such strategies offer numerous benefits. Companies can avoid wasting resources, improve focus and drive long-term success if they start implementing effective portfolio management strategies. In Agile environments, product portfolio management ensures that decisions align with evolving market needs and keep teams responsive and efficient.
Let’s look at some successful product management strategies next.
Strategies for successful product portfolio management
A well-defined product portfolio strategy helps companies increase market share and revenue by guiding how products are developed and positioned. Businesses typically take one of two approaches:
- Incremental growth – Focuses on low-cost expansions, such as enhancing or repackaging existing products to capture adjacent markets.
- Disruptive growth – Aim for high-impact innovation, either by developing groundbreaking products or acquiring new technology to reshape the market.
Here are some proven product portfolio strategies:
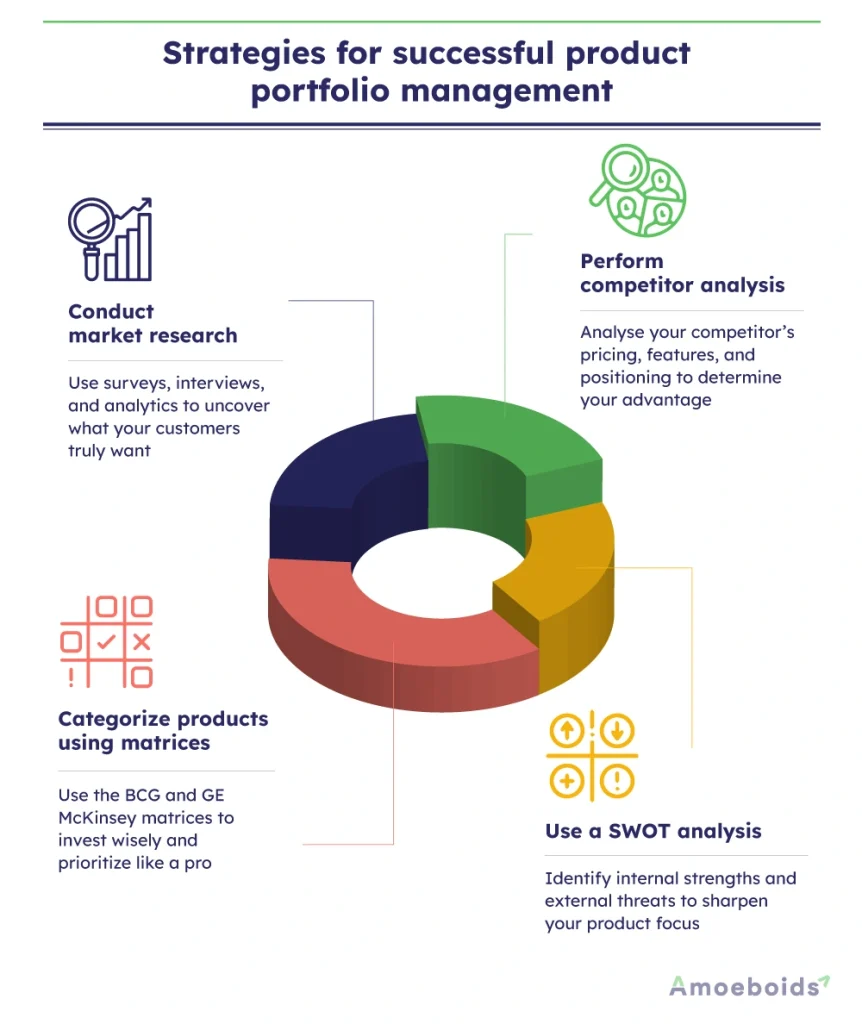
1. Conduct market research
Understanding customer needs and market trends is the foundation of a strong product portfolio strategy.
Tip: Use surveys, interviews and analytics to gather qualitative and quantitative insights from customers.
2. Perform competitor analysis
Analyzing direct and indirect competitors helps businesses identify gaps and opportunities.
Tip: Score competitors based on their product functionality, pricing and market positioning to find differentiation points.
3. Use a SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) helps businesses evaluate their existing product portfolio and determine where to improve.
Tip: Map out internal strengths (unique features, strong branding) and external threats (market shifts, emerging competitors).
4. Categorize products using matrices
- Growth-Share Matrix (BCG Matrix)
Developed by Boston Consulting Group, this framework helps classify products based on profitability and market potential:
- Stars – High growth, high market share (deserves major investment).
- Cash cows – Steady earners (maximize efficiency and profitability).
- Dogs – Declining products (consider transformation or phase-out).
- Question marks – High potential but uncertain success (requires careful investment decisions).
Tip: Regularly reassess products to shift resources from low-value to high-impact initiatives.
- GE McKinsey Matrix
A nine-box framework that evaluates a product’s market attractiveness and competitive strength. It’s useful for prioritizing investment in diverse product lines.
Tip: Use this for complex product portfolios with multiple market segments to make data-driven decisions.
Challenges in product portfolio management
Even with a solid product portfolio strategy, managing multiple products isn’t easy. Here are some real challenges businesses face:
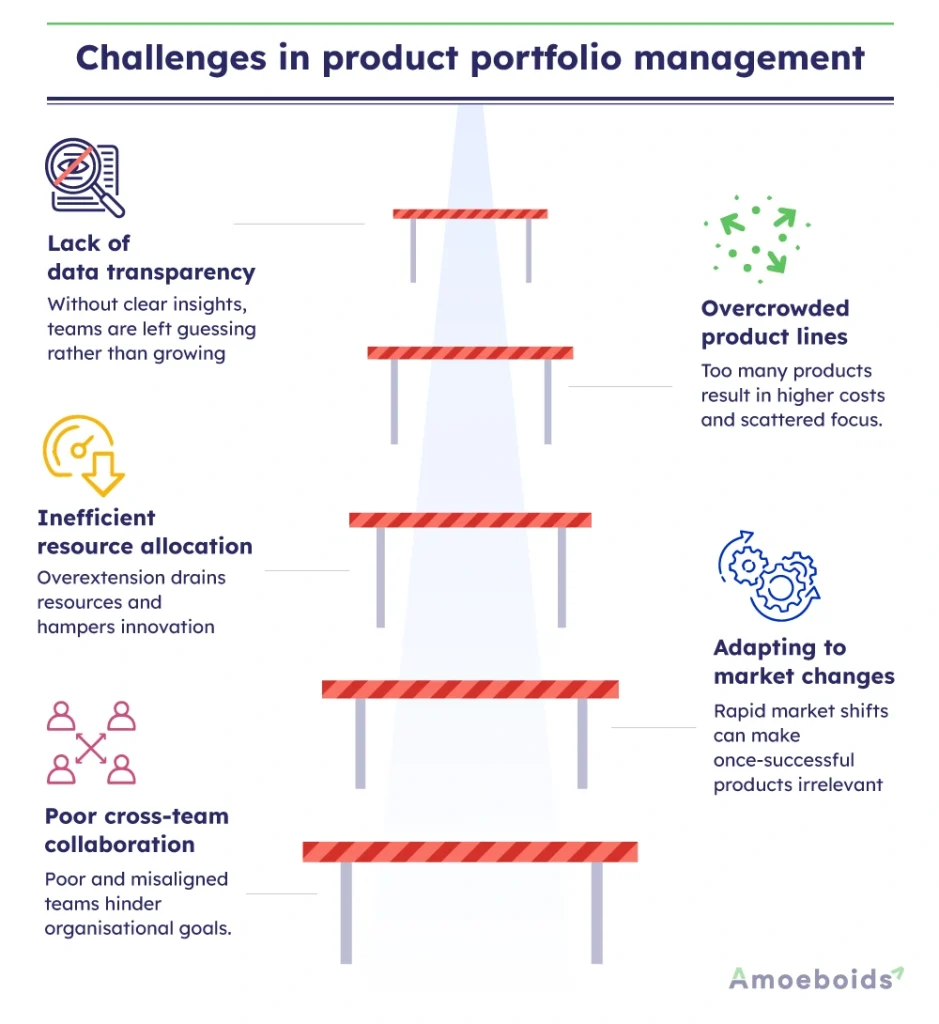
1. Lack of data transparency
- Without clear insights, teams struggle to make informed decisions.
- Example: General Electric struggled with unclear insights into its vast product portfolio, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities.
2. Overcrowded product lines
- Too many products equals higher costs and scattered focus.
- Example: Coca-Cola discontinued 200+ underperforming brands, including Tab and Odwalla, to focus on profitable products.
3. Inefficient resource allocation
- Spreading teams too thin slows innovation and lowers efficiency.
- Example: Sony overextended itself by launching too many Walkman variations, leading to confusion and resource drain.
4. Adapting to market changes
- Rapid shifts in demand can make once-successful products irrelevant.
- Example: BlackBerry’s failure to evolve its product portfolio strategy led to its decline.
5. Poor cross-team collaboration
- Disconnected teams lead to misaligned goals for your organization.
- Example: Boeing faced major setbacks with the 737 MAX due to misalignment between engineering and management teams.
Every company faces product portfolio management challenges, but strategic decisions guided by mental models for Product managers can prevent costly mistakes.
What are some examples of company product portfolios?
Understanding how companies structure their product portfolios can provide valuable insights into effective product portfolio management. Let’s explore two vastly different yet similar examples when we talk about product portfolios:
1. Apple Inc.
Apple is renowned for its cohesive and innovative product portfolio. Starting with personal computers, Apple expanded to include a range of consumer electronics and services that integrate seamlessly. Key products include:
- iPhone: A line of smartphones that have set industry standards.
- MacBook: A series of laptops known for performance and design.
- iPad: Tablets that bridge the gap between laptops and smartphones.
- Apple Watch: Smartwatches that offer health tracking and connectivity.
- Services: Including iCloud, Apple Music and the App Store.
This diversified yet interconnected product portfolio makes Apple a successfully running, robust ecosystem with cross-product integration.
2. Amoeboids
Amoeboids is a great example of product portfolio management done right. We’ve built a suite of apps designed to boost productivity and collaboration within the Atlassian ecosystem. Here’s a look at what we offer:
- Automated Release Notes & Reports: Streamlines the creation and distribution of release notes, reports directly from Jira.
- Embedder for Confluence: Enables teams to integrate Confluence content into external platforms.
- Roadmap & Idea Portal: Facilitates collaboration with customers to build compelling public or private product roadmaps via Jira Service Management.
- Screenjar for Jira: Allows users to attach screen recordings to Jira issues and service management tickets without additional installations.
- Release Planning & Reports: Assists teams focused on iterative delivery to maintain consistent value shipment to customers.
Amoeboids focuses on tools that integrate smoothly with Atlassian products. It addresses specific needs across various roles, from customer support to product marketing. This targeted approach ensures the product portfolio remains relevant and valuable to the user base.
Conclusion
A cluttered product portfolio can drain resources, slow innovation, and leave teams scrambling to keep up. But with the right product portfolio management strategies, you can turn scattered products into a well-oiled machine – one where every offering has a purpose, every investment is intentional and data backs every decision.
Companies like Apple show that a well-managed product portfolio creates long-term success by aligning innovation with customer needs. Refining an existing portfolio or building one from scratch, the key is to stay agile, data-driven and customer-focused.
FAQs
What is a balanced product portfolio?
A balanced product portfolio is a mix of high-growth, steady-revenue and experimental products. Its objective is to minimize risk and maximize profitability.
What is a good design for a product design portfolio?
A strong product design portfolio showcases diverse projects, highlights problem-solving skills and clearly explains design decisions with real-world impact. Choose only the strongest pieces that are the most unique, innovative, and creative.
How to analyze a product portfolio?
You can use frameworks like the BCG Matrix or SWOT analysis to assess performance, profitability and market fit. It helps you decide where to invest or cut losses.