Release management is a systematic process that involves overseeing the entire lifecycle of software from development to production. It helps organizations deliver high-quality products while minimizing risks associated with software deployment. It’s about ensuring everything works as expected with no odd surprises. With good release management, your updates roll out without a hitch, and users stay happy.
In this guide, we’ll explain release management, how it works, the best practices, common challenges, tools, and how to measure success.
What is release management?
Release management outlines the systematic process of building new and updating software products. It is the process of planning and handling software updates. It ensures that everything works properly before the update is released. Whether you are rolling out IT services, products or updates, this is a process that helps you effectively manage the project.
Release management creates a more efficient process, resulting in shorter times to market and fewer quality problems. Ultimately, that means your company can be more responsive to market changes and consumer preferences by increasing the number of successful releases. By mitigating risk, effectively managing releases ensures the customer experience remains consistent throughout the roll out process.
The key stakeholders involved in release management are:
- Product managers: They decide what features or fixes should be included in the release.
- Development teams: They are the ones building and coding the updates.
- QA teams: They test the updates to catch any bugs or issues before release.
- Operations teams: They handle the deployment and monitor the app after updates.

How does it compare to project management?
If you are thinking release management sounds a lot like project management, you’re right. They are both essential to a successful product rollout. However, they each play their own vital role.
| Aspect | Project Management | Release Management |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Planning and coordinating resources to launch a product or release successfully. | Coordinating test, production, and IT environments to deploy products with minimal disruption. |
| Scope | Broad focus on the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to closure. | Specific focus on the transition of projects from development to production environments. |
| Key Responsibilities | – Planning resources- Scheduling tasks- Managing risks- Monitoring progress- Delivering outcomes | – Coordinating environment configurations- Ensuring seamless deployment- Handling IT environment changes |
| Objective | Delivering a successful project within constraints like budget, scope, and time. | Creating a proactive, predictable environment for seamless IT changes and ensuring end-user functionality. |
| Team Involvement | Managed by a dedicated project manager or team, often involving cross-functional stakeholders. | Managed by a specialized release team or integrated into the project team, depending on complexity and resources. |
Now that we understand the basics of release management let’s look at the release management cycle and its overall process.

Release management process for software
Release management process consists of various essential steps that ensure everything operates as intended, with minimal inconvenience to users. Let’s analyze these phases:
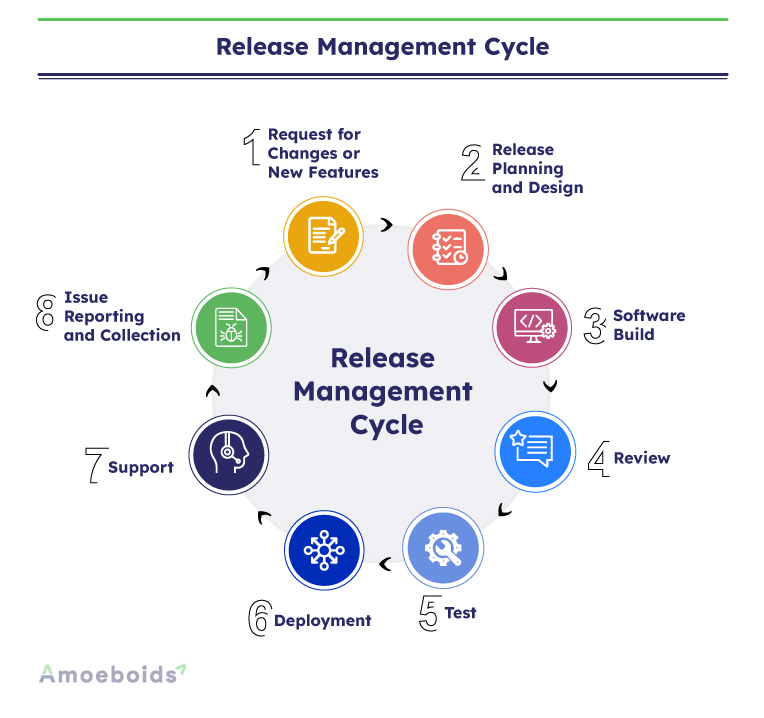
Planning
In the planning phase, the team notes the scope of the next release, including which new features or fixes will be included. They also assess potential risks, like system compatibility issues, to prepare solutions in advance.
Pro Tip: Start by outlining standards and requirements. Create a workflow that includes timelines, delivery dates and requirements, as well as the project’s overall scope. Craft your plan according to what works best for your team. Use agile release planning to plan incremental releases of a product.
For example, you may opt for a checklist that chronologically outlines processes and responsibilities. Another option is to create a cloud-based flowchart that contains the same information in a more visual format.
Once this phase is complete (convey the upcoming changes via release notes preview), get feedback from all stakeholders and make needed adjustments.
Building
Once the plan is in place, development begins. The team works on rolling out new features or fixes identified during planning. This phase also involves integrating new features with the existing system, ensuring no disruption to the app’s overall functionality.
Pro Tip: Automate integration processes using CI/CD tools to ensure consistent builds and reduce manual errors. Collaboration platforms like Slack or Teams streamline communication between developers and other stakeholders.
Testing
After development, rigorous testing ensures functionality and security. User acceptance testing (UAT) gathers feedback from a select group of end users, often via beta trials.
Pro Tip: Leverage automated testing tools to run regression, performance, and security checks faster. Use feedback forms or analytics platforms during UAT to capture actionable insights seamlessly.
Deployment
Once testing is complete, the update is deployed to users. Often, the release is rolled out to a smaller group (e.g., canary deployment) before a full-scale launch. Release notes or guides help users adapt to changes.
Pro Tip: Automate deployment pipelines for efficient rollouts, minimizing downtime and errors. Maintain clear communication via release notes or in-app notifications to educate users about the update.
Monitoring
Post-deployment, the team monitors the app’s performance, user reactions, and any bugs that may arise. Prompt issue resolution is critical to maintaining system stability.
Pro Tip: Use monitoring tools like New Relic or Dynatrace to automate performance tracking and issue detection. Establish a feedback loop with users to quickly identify and address pain points.
Key challenges in release management
Release management often comes with hurdles that teams must navigate effectively to ensure a smooth deployment. Here are some of the main challenges:
- Handling tight deadlines and limited resources: Teams frequently face the pressure of delivering on aggressive timelines while managing limited resources. This can strain planning, execution, and quality assurance efforts.
- Managing dependencies across teams: Coordinating activities among multiple teams—such as development, QA, and IT—can be complex. Misalignment or communication gaps can result in delays or missed objectives.
- Balancing speed with quality assurance: Striking the right balance between rolling out updates quickly and ensuring they meet quality standards remains a persistent challenge for release managers.
- Tracking and addressing post-release issues: Even with thorough planning, unforeseen issues can arise post-deployment. Addressing and resolving these quickly is critical to maintaining system stability and user confidence.
By recognizing these challenges, teams can implement strategies to address them effectively. The next section will delve into proven techniques to overcome these hurdles.
Essential tools and add-ons for streamlined release management
Let’s review some tools that streamline release management for teams of any size, helping them deploy products faster and more efficiently:
Jira
Jira is widely used for overseeing release planning, tracking progress, and generating detailed reports. It helps teams allocate tasks, monitor issues, and assess the status of each phase in the release cycle. With Jira, teams can ensure every part of the release process is well-documented and transparent.
Add-ons for Jira:
- Automated Release Notes for Jira: This add-on from Amoeboids automates the process of creating release notes, saving teams significant time. It generates customizable release notes directly from Jira issues, making the documentation process seamless and reducing manual errors.
- Release Planning and Reports for Jira: This add-on from Amoeboids helps teams easily plan, manage, and track releases. It allows users to visualize the release pipeline, prioritize tasks, and generate reports that offer real-time insights into the status of ongoing releases. The integration simplifies release management, ensuring alignment with business goals and timelines.
GitHub/GitLab
GitHub and GitLab are essential for version control and automated deployment workflows. These platforms allow developers to work on features without interfering with active code. GitLab takes it further by offering CI/CD pipelines, automated code testing, and deployment tools that enhance release cycle efficiency.
Confluence
Confluence is a centralized hub for exchanging release strategies, specifications, and technical documentation. It ensures that all team members can access the latest updates and are aligned throughout the product development process, facilitating smooth collaboration.
Now that we have an idea about some of the essential tools for release management, let’s look at what metrics are used to measure its success.
Metrics to measure release success
To evaluate the effectiveness of your release cycle, consider these four key metrics:
Release Frequency
Measures how often updates are deployed to production. A consistent release schedule indicates a healthy development pipeline, ensuring regular updates that add value. However, releases that are too frequent might overwhelm users. Striking the right balance keeps users engaged and satisfied.
Lead Time for Changes (LTFC)
Tracks the time it takes for a feature to move from ideation to deployment. Shorter lead times are preferable, as they reflect an efficient development and testing process. Prolonged lead times may signal bottlenecks or inefficiencies. Optimizing LTFC keeps your team agile and responsive to user needs.
Change Failure Rate (CFR)
Indicates the percentage of deployments that lead to post-release issues. A high CFR suggests a need for better testing or quality control. For instance, refining your testing protocols becomes crucial if one in five updates results in a crash. Keeping this rate low fosters trust and ensures smoother releases.
Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR)
Measures how quickly teams resolve issues after a release. A low MTTR reflects strong problem-detection and resolution capabilities, minimizing downtime and user frustration. Fast recovery times are essential, particularly for mission-critical systems. Monitoring MTTR enhances overall release effectiveness.
To conclude
Effective release management is the backbone of successful software deployment. By implementing a structured process, leveraging the right tools, and tracking key metrics, teams can ensure smooth releases that delight users while minimizing risks.
As software development evolves, staying proactive and adaptive in your release strategies is essential for maintaining stability, building user trust, and driving growth. With thoughtful planning and execution, your release process can become a competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
FAQs
What is release management in software development?
Release management is the process of planning, scheduling, and overseeing software updates to ensure they are deployed effectively with minimal disruption.
What are the stages of the release management process?
The process typically involves five stages:
- Planning: Setting objectives, timelines, and boundaries.
- Building: Developing features or fixes.
- Testing: Ensuring functionality, security, and quality.
- Deployment: Launching updates to users.
- Monitoring: Observing performance and collecting feedback.
How do you handle risks in release management?
Managing risks involves identifying potential issues during the planning phase, conducting thorough testing, and preparing contingency plans. Post-deployment monitoring enables quick resolution of unexpected problems.
What tools are best for release management?
Top tools include Jira, GitHub/GitLab, Confluence, LaunchDarkly, and Azure DevOps. These platforms streamline tracking, collaboration, automation, and deployment.
How do you measure the success of a release?
Use metrics like release frequency, lead time for changes, change failure rate, and mean time to recovery to assess the efficiency, reliability, and impact of your release process.


