Understanding the roles and responsibilities of a product manager is crucial for anyone involved in product development. This multifaceted role is the linchpin for the entire product lifecycle, ensuring a seamless journey from concept to launch.
New product launches are frequent in today’s crowded marketplace, but success is rare. According to MIT, approximately 30,000 products are launched annually, yet only 5% succeed. A skilled and proactive product manager can distinguish between a groundbreaking success and a missed opportunity.
Often seen as innovators, product managers are the driving force behind transforming ideas into market-ready solutions. In this blog, we’ll explore their core responsibilities and how effective product management can pave the way for success. Let’s get started!
What does a product manager do?
Martin Eriksson, a veteran product leader and founder of ProductTank, famously described the product manager’s role as being “at the intersection of business, technology, and user experience,” balancing the needs of all three.
Product managers are versatile professionals who juggle multiple roles. They rely on their strategic mindset, market insight, and leadership skills to drive a product’s success. At their core, they must deeply understand the product and its features to ensure it aligns with customer needs and the organization’s business goals.
Key responsibilities include overseeing the entire product launch process, from ideation to execution. This involves crafting a well-rounded product launch strategy designed to maximize impact and deliver successful outcomes for the business. Let’s discuss these in detail.
10 key responsibilities of a product manager
A product manager’s role extends beyond strategy and execution; it involves adapting to the organization’s scale and structure. In larger organizations, product managers act as orchestrators, working closely with specialized teams—such as researchers, marketers, designers, and developers—who handle distinct aspects of the product cycle, from gathering insights to refining prototypes.
In contrast, in smaller setups, product managers often adopt a more hands-on approach, wearing multiple hats and directly overseeing everything from ideation to delivery. Despite these differences, their core responsibility remains the same: maintaining ownership of the product, ensuring its alignment with the vision, and making pivotal decisions to drive success.
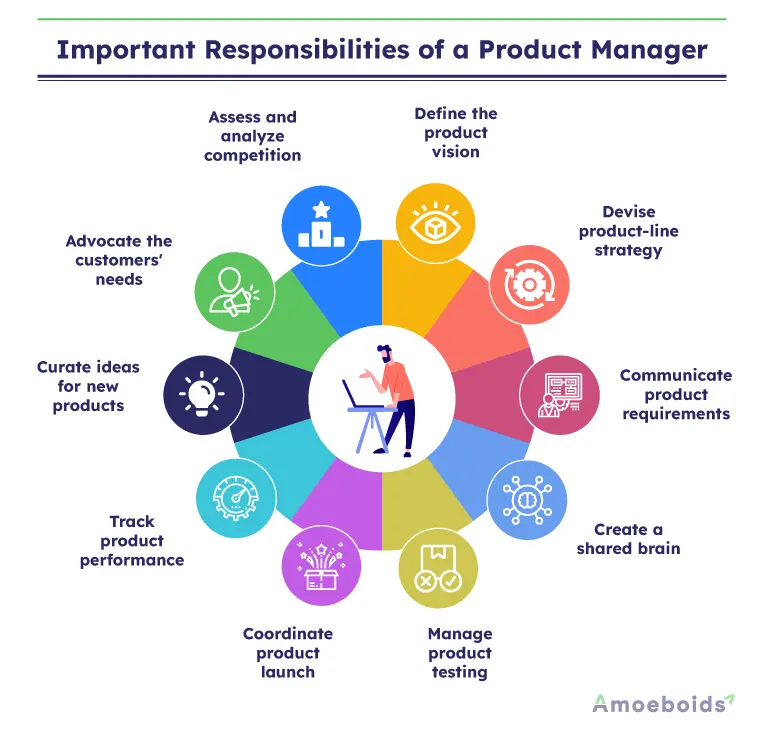
Let’s take you through the 10 critical responsibilities of a product manager:
- Curate ideas for new products: Gather product insights and market intelligence to curate viable ideas for new products and innovative features.
- Advocate the customers’ needs: Understand the product’s market to articulate and prioritize the user’s requirements.
- Assess and analyze competition: Monitor and analyze market data to understand competition and unique products that meet the industry benchmarks.
- Define the product vision: Create a unique product positioning and share it with the marketing team to chart the product’s roadmap.
- Devise product-line strategy: Define production schedules, and maintain and adjust them to meet timelines.
- Communicate product requirements: Share customer needs with the engineering and support teams to create distinctive products or enhance existing features.
- Create a shared brain: Align all stakeholders, including engineering, sales, marketing, and support, around the shared vision for the product.
- Manage product testing: Collaborate with the technical team to review the product, detect and fix bugs and make necessary improvements. Run beta and pilot programs with samples and final products.
- Coordinate product launch: Bring all teams together to launch the product successfully and on time.
- Track product performance: Gather customer feedback to track the product’s performance and make further improvements.
Best practices for new product managers
For new product managers, focusing on key areas is essential to building a solid foundation for success. Adopting industry best practices is the most effective way to become more efficient and skilled. Here are some top practices to guide you:
1. Focus on learning
Embrace continuous learning. Attend seminars, stay updated on industry trends, and seek mentorship. This will not only enhance your skills but also help you stay adaptable in an ever-changing market.
2. Build strong relationships with teams
Success as a product manager relies heavily on effective collaboration. Foster strong relationships across cross-functional teams, whether in marketing, engineering, or sales. Open communication and mutual respect lead to more harmonious and productive teamwork.
3. Adopt a problem-solving mindset
Handling challenges like technical issues or market changes requires a solution-focused approach. Think critically and creatively, and always base your decisions on data to navigate obstacles effectively.
4. Stay customer-centric
Always keep the customer at the center of your decision-making. Understand their needs, collect feedback, and use it to drive product improvements. A customer-centric approach ensures your product remains valuable and relevant, driving its success in the market.
Go-To-Market (GTM) approaches for product managers
A Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines how an organization will introduce a product to the market, acquire its target audience, and secure a competitive advantage. It ensures that the product meets market needs and gains acceptance. A successful GTM strategy is built on a deep understanding of the competitive landscape, customer preferences, and market trends. Here are key actions product managers should take to develop a winning GTM approach:
1. Develop positioning and messaging
Create clear, compelling messaging that highlights your product’s unique value proposition. Strong positioning speaks directly to your target market and differentiates your product from competitors, making it stand out in a crowded space.
2. Design pricing models
Establish competitive pricing strategies that align with your product’s value. Consider factors like production costs, customer affordability, and competitor pricing to craft a model that resonates with your target audience while maintaining profitability.
3. Provide tools and training for sales teams
Equip sales teams with the necessary tools, resources, and training to effectively market the product. This includes training on key selling points, product demos, and providing sales collateral that reinforces the product’s value.
4. Build a robust marketing plan
Create a comprehensive marketing plan that includes strategies for public relations, content creation, digital marketing, and social media. The goal is to generate product awareness and drive demand through targeted campaigns.
5. Set timelines and KPIs
Implement the product launch with well-defined timelines and key performance indicators (KPIs). Establish a clear schedule with measurable benchmarks to track progress, ensuring all teams are aligned for a seamless and impactful launch.
6. Monitor market response
Evaluate post-launch market response to refine your strategy. Collect feedback from customers and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. Based on this feedback, continuously update your GTM approach to enhance customer satisfaction and product performance.
Product managers must navigate the complexities of product launches while ensuring effective customer segmentation. By focusing on these essential steps, they can maximize their product’s success in the market.
Customer segmentation examples for product managers
Segmenting customers is a key pillar of any successful product management strategy. Customer segmentation is inevitable as a product manager aiming to boost user engagement and secure buy-in. Here are some primary customer segmentation methods used in the industry:
1. Demographic segmentation
This method divides the target audience based on demographic factors like age, gender, income, education, occupation, and marital status. By understanding these attributes, product managers can tailor the product launch plan to address the unique needs of different demographic sectors.
2. Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation groups the audience based on their interests, values, attitudes, and personality traits. This approach helps understand deeper motivations and behaviors, allowing product managers to craft messaging that resonates more effectively with distinct consumer groups.
3. Behavioral segmentation
While similar to psychographic segmentation, behavioral segmentation focuses on customer purchase behaviors, usage patterns, brand interactions, loyalty, and readiness to buy. By analyzing these behaviors, product managers can create more targeted strategies and successful product launch plans that meet customer expectations.
4. Geographic segmentation
Focusing on geographic factors such as country, region, city, climate, and urban/rural location enables product managers to customize the product launch according to local tastes, preferences, and demands. This approach is essential for catering to varying regional needs.
Using these segmentation techniques helps product managers develop focused, successful launch plans, ensuring the product appeals to the right market segments and achieves strong market penetration.
What makes a product manager successful?
Several key qualities define effective product managers in the ever-evolving field of product management:
1. Customer empathy
Customer empathy is vital as it allows product managers to understand and address customer needs. Empathy ensures that the product genuinely solves consumer problems and improves their experience.
2. Analytical and data-driven mindset
A successful product manager makes decisions based on customer feedback and market data. By utilizing an analytical and data-driven approach, they can identify trends and insights that inform smarter product strategies.
3. Excellent communication skills
Strong communication skills are essential for aligning teams and articulating the product vision. Clear communication helps ensure everyone is working toward the same goals and objectives.
4. Strong technical knowledge
A deep understanding of technical aspects enables product managers to make informed decisions and collaborate effectively with development teams. It allows them to bridge the gap between business and technical requirements.
5. Adaptability in dynamic environments
Product managers must be adaptable to changing market conditions, customer demands, and team dynamics. The ability to pivot strategies while staying focused on the product vision is crucial for success.
Balancing a clear product vision with practical implementation ensures a blend of innovation and feasibility in the product launch process. These qualities equip product managers to meet their responsibilities and lead successful product introductions.
Conclusion
Successful product management hinges on a deep understanding of customer segmentation, a focus on core qualities like empathy and communication, and the ability to execute a well-rounded go-to-market strategy. By continuously learning, building strong cross-functional relationships, and staying adaptable, product managers can drive their products toward success.
Through thoughtful segmentation and a customer-centric approach, they can ensure that every product launch resonates with the right audience and meets business and consumer needs. Ultimately, these practices enable product managers to lead their teams and products confidently and clearly.
FAQs
Q1: How do a product owner and a product manager differ from one another?
A product owner concentrates on agile sprint tasks, while a product manager is dedicated to shaping the overall product vision and strategy.
Q2: Which tools are utilized by product managers?
Essential tools for effective road mapping, project management, and analytics include Aha! for road mapping, Jira and Trello for project management, and Google Analytics and Mixpanel for analytics.
Q3: What does a typical career trajectory look like for a product manager?
A standard career path for a product manager is: Associate Product Manager → Product Manager → Senior Product Manager → Director of Product → VP of Product → Chief Product Officer.
Q4: What qualities define an effective product manager?
Key qualities include empathy, effective communication, data-driven decision-making, and adaptability.
Q5: Which books are essential for product managers?
Recommended books include Inspired by Marty Cagan, Hooked by Nir Eyal, and Measure What Matters by John Doerr.


