In a world where innovation is key, who drives the success of a product from concept to reality?
Product managers are at the heart of this innovation, guiding products from inception to market success.
As the tech industry continues to expand, the need for skilled PMs is on the rise, making this role more critical than ever.
Understanding the career trajectory of a product manager (not to be confused with product owner) is essential for those looking to thrive in this dynamic field.
This post breaks down the career path of a product manager in three categories – Entry level, mid-level & senior level. We also make it a point to include relevant job descriptions, skill sets & other nuances of the trade.
Typical career path for Product Managers
First & foremost, job titles in product management can vary deep & wide. Given how nascent the function is, don’t expect consistency in how different organizations name their positions. it is quite possible that an associate product manager at one org is doing the same job as that of a junior product manager at another company. And so on.
Some small businesses may even integrate the product manager responsibilities into other roles such as project, delivery or program managers.
Despite these variations, understanding a general career path for Product Managers can still be immensely valuable.
It helps in mapping out your career trajectory and planning your professional growth, regardless of the specific titles used in your organization.
Here’s a roadmap to guide you through the typical career path and alternative routes that can shape your professional trajectory in this exciting field.
Entry-level product management positions
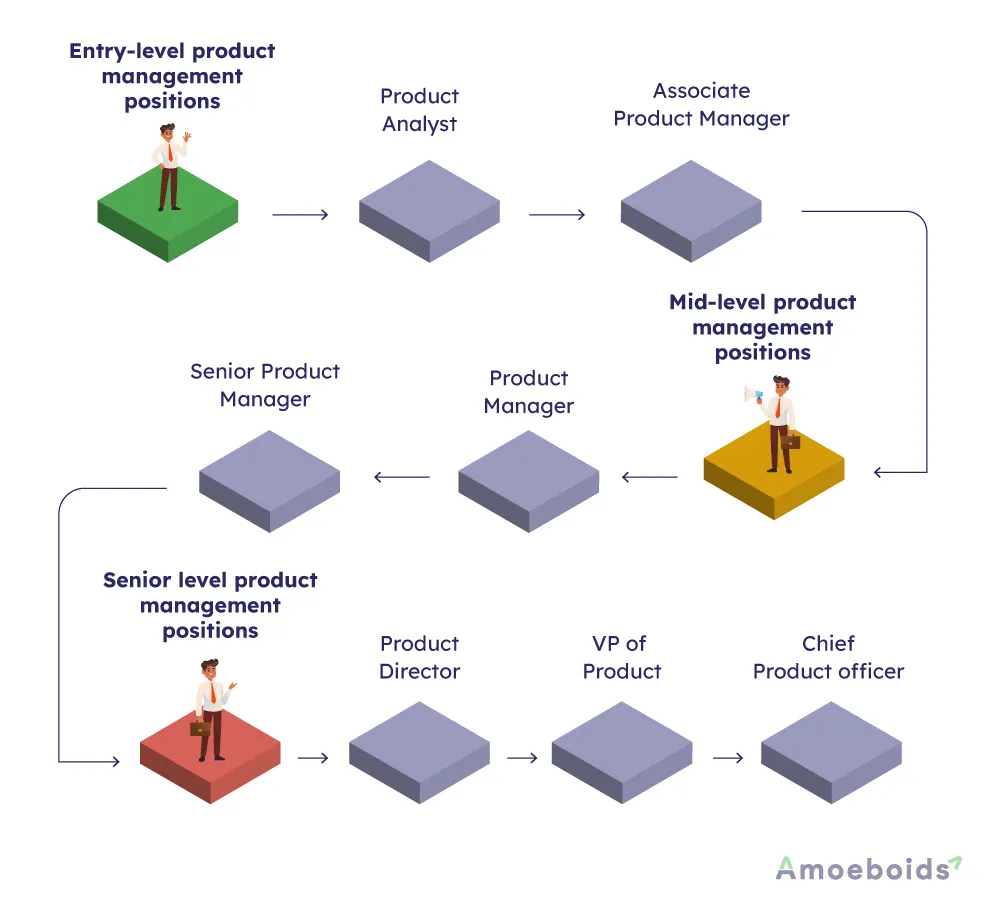
1. Product Analyst
A product analyst primarily looks at data to offer insights that help with product decisions.
To support strategic choices and product improvement, this position involves assessing user behavior, monitoring market trends, and evaluating product performance.
Responsibilities:
Data analysis: Analyze data around various aspects of the product and come up with actionable insights for improvements. The data can range anywhere from general product usage to specific user interactions as well customer responses to product feedback surveys,
Reporting: Create and provide dashboards, reports for stakeholders to share findings and sway their opinions about product improvements & future products.
Market research: Gather & analyze information to comprehend consumer demands, industry trends, and the competitive environment.
Support: Work together with mid & senior level product managers to establish strategies and offer recommendations that are supported by data.
Ideal background:
- Proficiency with data analysis software & tools (such as SQL and Excel).
- Familiarity with competition analysis and market research.
- A degree in business, statistics, data science, or a similar discipline.
2. Associate Product Manager
An associate product manager assists with product management tasks on a lesser scale than a product manager.
The duties of the position include helping product managers establish priorities, managing daily operations, and fostering close relationships with cross-functional teams.
Responsibilities:
Prioritize tasks: By managing them within predetermined boundaries and making sure they are in line with the objectives of the product. Do note that strategic tasks are off limits since they are the responsibility of senior product managers.
Collaboration: To assist the development and execution of product development, collaborate closely with the engineering, UX, and product teams.
Communication: Balance customer needs with company objectives by keeping stakeholders updated on project status and concerns.
Metrics monitoring: Monitor and assess product performance and features with the help of data to make sure goals are reached.
Ideal background:
- Strong communication and organizing abilities.
- It helps to have project management or product marketing experience.
- A degree in business, computer science, or a similar discipline that is relevant.
Recent graduates who are enthusiastic and possess relevant abilities are also considered.
Mid-level product management positions
3. Product manager
Primary responsibility of a product manager is assisting the senior management in execution of product strategy.
They ensure that the product satisfies user needs and business objectives by serving as the main point of contact for the product team and other stakeholders.
Responsibilities:
Execute product strategy: While product managers do assist in defining the product strategy, their primary responsibility is executing it.
Project & product roadmap management: Keep an eye on a product’s complete development process, from conception to launch, to make sure it stays on schedule and satisfies business goals. They also take ownership of driving the product roadmap forward.
Stakeholder communication: Consult with stakeholders to improve strategy and stay informed about goals and product progress.
Market and user research: To guide product decisions and enhancements, analyze market trends, user feedback, and the competition.
Ideal background:
- Proven experience in product management or related roles.
- Strong skills in project management, communication, and strategic planning.
- Experience with data analysis and product metrics to drive decisions.
4. Senior product manager
A senior product manager leads the team that develops and implements the product vision.
They oversee more complicated or large-scale deliverables, provide junior team members with guidance, and spearhead strategic projects.
Responsibilities:
Leadership and mentoring: Help develop a powerful, cooperative work environment by offering relatively inexperienced product managers and other team members guidance, leadership.
Advanced stakeholder management: Talk to important stakeholders and top executives to get resources and support for your product objectives.
Making strategic decisions: Make significant choices about trade-offs, investments, and product features while keeping company priorities and user demands in mind.
Innovation and optimization: Promote innovation by investigating novel avenues and refining current product attributes considering customer input and industry developments.
Ideal Background:
- Several successful product launches to show extensive experience in product management.
- Ability to influence and align diverse teams and stakeholders around product goals.
Senior level product management positions
5. Product director
Managing a broad product portfolio or several product lines falls within the purview of a product director.
They establish strategic direction, match business objectives with product initiatives, and guarantee that at the macro level their product portfolios satisfy consumer and market demands.
Responsibilities:
Strategic oversight: Create and implement a broad product plan for a line of products or a variety of products, ensuring that it aligns with corporate goals.
Leadership: Oversee and coach teams and product managers to promote growth and guarantee that product strategies are carried out successfully.
Cross-functional coordination: Work with other departments to ensure smooth product development and successful GTM execution.
Performance monitoring: Monitor the performance of their products using KPIs and metrics, and adapt the tactics in response to market feedback and data.
Budget management: Manage investments, distribute resources, and keep an eye on product budgets to maximize product results.
Ideal Background:
- Substantial background in product management and a track record of overseeing teams and managing complicated products.
- Strong leadership, ability to make high impact decisions, and strategic thinking skills.
- Demonstrated capacity to oversee complex projects and get outcomes.
6. VP of Product
A senior executive in charge of the company’s entire product strategy and vision is the vice president of products.
They collaborate closely with the leadership team to generate growth and match product ambitions with business goals.
Responsibilities:
Vision and strategy: Create and share a long-term product vision and strategy that is in line with the business objectives and market prospects of the organization.
Executive leadership: Work together with other senior executives to drive company-wide initiatives and combine product plans with overall company strategy.
Team management: Establish and oversee a productive group of product managers while offering possibilities for professional growth and assistance.
Innovation and growth: To propel business growth, seek for and seize new product developments, market expansions, and business opportunities.
Engagement with stakeholders: To coordinate product strategies and obtain input, interact with important stakeholders like investors, partners, and customers.
Ideal Background:
- A great track record of strategic impact and team management, along with extensive experience in leadership and product management roles.
- Outstanding executive presence, strategic thinking, and stakeholder impact.
- Proven success in generating product growth and innovation.
7. Chief product officer
The top executive in charge of the entire product organization is the Chief Product Officer .
They set the overall strategic direction for all product efforts and ensure that product development aligns with the business’s goals.
Responsibilities:
Leadership in organization: Oversee and grow the product management team, including recruiting, coaching, and supervising senior product managers.
Cross-company integration: Make sure product strategies relate to overall business strategy and operations by collaborating closely with other C-level executives.
Market and customer focus: Promote customer input, make sure products fulfill consumer needs, and increase customer happiness.
Performance and metrics: Track and evaluate business results and product performance, making necessary adjustments to strategy to maximize growth and success.
Ideal background:
- Extensive background in top product management positions and a proven track record of directing strategic initiatives and product organizations.
- Outstanding organizational, strategic thinking, and leadership abilities.
- Demonstrated capacity to influence the entire organization and match product strategy with overarching business objectives.
Various Product management designations across organizations
Your understanding of a product manager’s tasks and career advancement may be impacted by the variety of titles that different firms use for similar positions.
For example, duties performed by a Product manager in one organization may be substantially like those of a Product analyst in another.
Analogously, a Product Coordinator is comparable to an Associate Product Manager in that they frequently oversee administrative duties and assist with project management.
An entry-level Associate Product Manager’s responsibilities are frequently similar to those of a Junior Product Manager, while a Product Associate typically provides product management support in ways similar to those of an Associate Product Manager.
Understanding these differences can enable you to better visualize a product manager’s career path or trajectory across various organizations.
Skills a Product manager needs for career progression
While some of the skills needed to grow in your product manager career path come from experience, there are others that are more fundamental. We list some of them below:
- Effective communication
- Strategic thinking
- Cross-functional collaboration
- Analytical skills & critical thinking
- Problem solving and Adaptability
Developing & honing these skills can help you advance your career in product management.
Challenges in the Product manager career path & how to overcome them
Product management is a career with its own set of challenges.
While you don’t necessarily need to be a coder, having technical know-how helps.
While you don’t necessarily need to be a UX researcher, some understanding always helps.
While you don’t need to be a seasoned project manager, having a good grasp on project management concepts helps.
While you don’t need to be a marketer, basics of product marketing go a long way in making you successful.
Early on, you may find it difficult to balance several obligations or grasp the entire range of your responsibilities.
To go past hurdles, look for guidance, grow your network, and improve your abilities.
As you advance, use your analytical abilities, interpersonal skills, and adaptability to tackle strategic and team-related problems.
Take appropriate measures to turn these problems into opportunities for progress.
Conclusion
A career path for a product manager is like an exciting journey; you start off as an associate product manager or product analyst.
The path changes with new opportunities and challenges as you go up the product manager career ladder like chief product officer or director of products.
Every level has a unique combination of obstacles and chances for development.
Accept each stage with an unwavering dedication to lifelong learning and adjustment.
To advance, look for guidance, hone your abilities, and discover fresh sources.
You can become an expert in product management if you continue to be proactive and involved.
Take advantage of every chance you get since the adventure will be both rewarding and entertaining!



